Introduction
In this article, we are going to create a cascading dropdown list in Blazor using Entity Framework Core database first approach. We will create two dropdown lists — Country and City. Upon selecting the value from the country dropdown, we will change the value of the City dropdown.
We will be using Visual Studio 2017 and SQL Server 2014.
Let’s take a look at the final product.
Prerequisites
- Install .NET Core 2.1 Preview 2 SDK from here
- Install Visual Studio 2017 v15.7 or above from here
- Install ASP.NET Core Blazor Language Services extension from here
- SQL Server 2008 or above
Blazor framework is not supported by versions below Visual Studio 2017 v15.7.
Source Code
Before proceeding, I would recommend that you get the source code from GitHub.
Creating Tables
We will be using two tables to store our data.
- Country: used to store the name of the Country. It contains two fields — CountryId and CountryName.
- Cities: This contains the list of cities for the Countries we will insert in the Country table. It contains three fields — CityId, CountryId, and CityName. The CountryId column is a foreign key referring to CountryId in the Country table.
Execute the following commands to create both tables:
CREATE TABLE Country(CountryId VARCHAR(5) PRIMARY KEY,CountryName VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL)GOCREATE TABLE Cities(CityId VARCHAR(5) PRIMARY KEY,CountryId VARCHAR(5) FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Country(CountryId),CityName VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL)GONow we will put some data in both of the tables. Open the Country table and execute the following insert statement.
INSERT INTO Country VALUES ('C1', 'India')INSERT INTO Country VALUES ('C2', 'China')INSERT INTO Country VALUES ('C3', 'USA')Then execute the following insert statements to insert data into the Cities table.
INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P1','C1','New Delhi')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P2','C1','Mumbai')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P3','C1','Chennai')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P4','C1','Hyderabad')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P5','C1','Bengaluru')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P6','C2','Beijing')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P7','C2','Shanghai')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P8','C2','Hong Kong')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P9','C2','Macau')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P10','C3','New York')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P11','C3','Chicago')INSERT INTO Cities VALUES ('P12','C3','Las Vegas')Create Blazor Web Application
Open Visual Studio and select File >> New >> Project.
After selecting the project, a “New Project” dialog will open. Select .NET Core inside the Visual C# menu from the left panel. Then, select “ASP.NET Core Web Application” from the available project types. Name the project “BlazorDDL” and press OK.
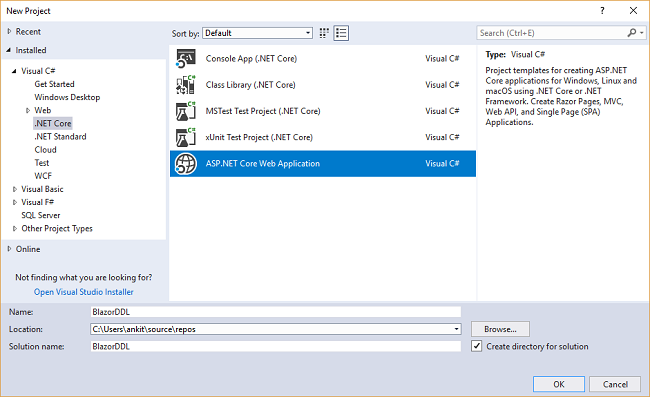
After clicking on OK, a new dialog will open asking you to select the project template. You can see two drop-down menus at the top left of the template window. Select “.NET Core” and “ASP.NET Core 2.0” from these dropdowns. Then, select the “Blazor (ASP .NET Core hosted)” template and press OK.
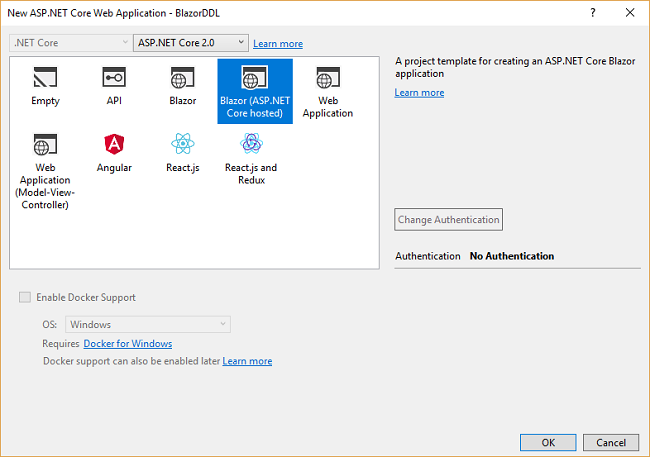
Now, our Blazor solution will be created. You can see the folder structure in Solution Explorer as shown in the below image.
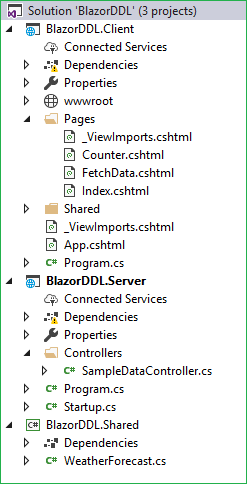
You can see that we have three project files created inside this solution.
- BlazorDDL.Client: it has the client side code and contains the pages that will be rendered on the browser.
- BlazorDDL.Server: it has the server side code, such as DB related operations and web API.
- BlazorDDL.Shared: it contains the shared code that can be accessed by both client and server.
Scaffolding the Model to the Application
We are using Entity Framework core database first approach to create our models. We will create our model class in the “BlazorDDL.Shared” project so that it can be accessible to both the client and server project.
Navigate to Tools >> NuGet Package Manager >> Package Manager Console. Select “BlazorDDL.Shared” from the Default project dropdown. Refer to the image below:
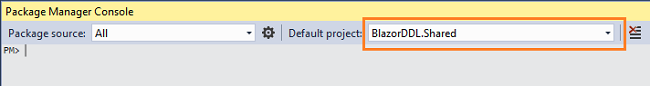
First we will install the package for the database provider that we are targeting, which is SQL Server in this case. Run the following command:
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServerSince we are using Entity Framework Tools to create a model from the existing database, we will install the tools package as well. Run the following command:
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.ToolsAfter you have installed both packages, we will scaffold our model from the database tables using the following command:
Scaffold-DbContext "Your connection string here" Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Models -Tables Country, CitiesDo not forget to put your own connection string (inside “ ”). After this command gets executed successfully, you can see that a Models folder has been created and contains three class files: “myTestDBContext.cs”, “Cities.cs”, and “Country.cs”. And so we have successfully scaffolded our Models using EF core database first approach.
At this point in time, the Models folder will have the following structure.
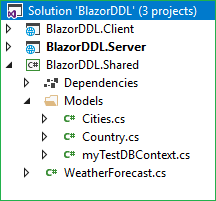
Creating the Data Access Layer for the Application
Right click on “BlazorDDL.Server” project and then select Add >> New Folder and name the folder “DataAccess”. We will be adding our class to handle database-related operations inside this folder only.
Right click on the “DataAccess” folder and select Add >> Class. Name your class “DataAccessClass.cs”. This class will handle our database-related operations.
Open “DataAccessLayer.cs” and put the following code into it.
using BlazorDDL.Shared.Models;using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace BlazorDDL.Server.DataAcces{ public class DataAccessLayer { myTestDBContext db = new myTestDBContext(); public IEnumerable<Country> GetAllCountries() { try { return db.Country.ToList(); } catch { throw; } } public IEnumerable<Cities> GetCityData(string id) { try { List<Cities> lstCity = new List<Cities>(); lstCity = (from CityName in db.Cities where CityName.CountryId == id select CityName).ToList(); return lstCity; } catch { throw; } } }}Here we have defined two methods:
- GetAllCountries: it will fetch all the country data from the country table.
- GetCityData: it will fetch the city data corresponding to the country id provided to it.
Now our data access layer is complete. We will proceed to create our web API Controller.
Adding the web API Controller to the Application
Right click on the “BlazorDDL.Server/Controllers” folder and select Add >> New Item. An “Add New Item” dialog box will open. Select “ASP.NET” from the left panel, then select “API Controller Class” from templates panel and name it “CountriesController.cs”. Press Add.
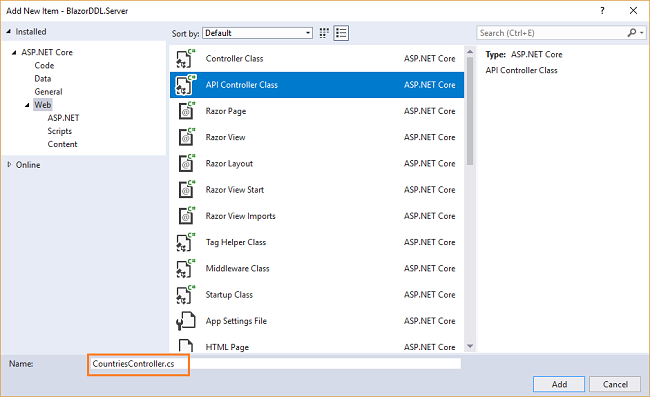
This will create our API “CountriesController” class.
We will call the methods of the “DataAccessLayer” class to fetch data and pass on the data to the client side.
Open the “CountriesController.cs” file and put the following code into it.
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Threading.Tasks;using BlazorDDL.Server.DataAcces;using BlazorDDL.Shared.Models;using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;namespace BlazorDDL.Server.Controllers{ public class CountriesController : Controller { DataAccessLayer objCountry= new DataAccessLayer(); [HttpGet] [Route("api/Countries/GetCountryList")] public IEnumerable<Country> GetCountryList() { return objCountry.GetAllCountries(); } [HttpGet] [Route("api/Countries/GetCities/{id}")] public IEnumerable<Cities> GetCities(string id) { return objCountry.GetCityData(id); } }}At this point in time, our BlazorDDL.Server project has the following structure.
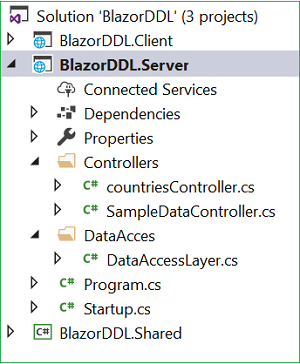
We are done with our backend logic. Therefore, we will now proceed to code our client side.
Adding Razor View to the Application
Right click on the “BlazorDDL.Client/Page”s folder and then select Add >> New Item. An “Add New Item” dialog box will open. Select Web from the left panel, then select “Razor View” from the templates panel and name it “CountryData.cshtml”.
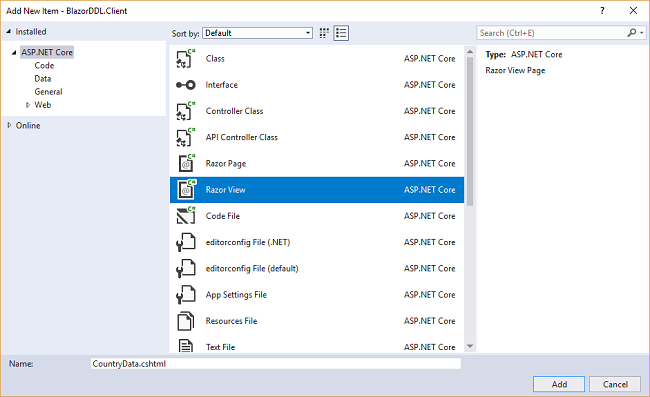
This will add a “CountryData.cshtml” page to our “BlazorDDL.Client/Pages” folder.
Open the “CountryData.cshtml” page and put the following code into it.
@using BlazorDDL.Shared.Models@page "/country"@inject HttpClient Http<h1>Country Data</h1><p>This component demonstrates cascading dropdownlist using EntityFrameWork Core</p><hr />@if (countryList == null){ <p><em>Loading...</em></p>}else{ <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-4"> <label for="Country" class="control-label">Country</label> </div> <div class="col-md-4"> <label asp-for="Cities" class="control-label">Cities</label> </div> </div> <div class="row" style="padding-top:10px"> <div class="col-md-4"> <select class="form-control" onchange="@CountryClicked"> <option value="">-- Select Country --</option> @foreach (var country in countryList) { <option value="@country.CountryId">@country.CountryName</option> } </select> </div> <div class="col-md-4"> <select class="form-control" onchange="@CityClicked"> <option value="">-- Select City --</option> @if (cityList != null) { @foreach (var city in cityList) { <option value="@city.CityName">@city.CityName</option> } } </select> </div> </div> <div class="row" style="padding-top:50px"> <div class="col-md-4"> <label class="control-label">Country Name: @countryName</label> </div> <div class="col-md-4"> <label class="control-label">City Name: @cityName</label> </div> </div>}@functions {List<Country> countryList = new List<Country>();List<Cities> cityList = new List<Cities>();string countryId { get; set; }string countryName { get; set; }string cityName { get; set; }protected override async Task OnInitAsync(){ countryList = await Http.GetJsonAsync<List<Country>>("api/Countries/GetCountryList");}protected async void CountryClicked(UIChangeEventArgs countryEvent){ cityList.Clear(); cityName = string.Empty; countryId = countryEvent.Value.ToString(); countryName = countryList.FirstOrDefault(s => s.CountryId == countryId).CountryName; cityList = await Http.GetJsonAsync<List<Cities>>("api/Countries/GetCities/" + countryId); this.StateHasChanged();}void CityClicked(UIChangeEventArgs cityEvent){ cityName = cityEvent.Value.ToString(); this.StateHasChanged();}}Let’s understand this code.
At the top, we have included BlazorDDL.Shared.Models namespace so that we can use our Country and Cities model class on this page. We define the route of this page using the @page directive. So, in this application, if we append “/country” to the base URL, then we will be redirected to this page. We are also injecting HttpClient service to enable the web API call.
Then we have defined the HTML section to display two Dropdown lists on our web page. We are calling the “CountryClicked” method on the “onchange” event of the Country dropdown. This method will call the “GetCites” web API method to fetch the city data from the Cities table corresponding to the countryid of the selected country.
We are also setting the value of the “countryName” property to the selected country. The “StateHasChanged” method is invoked to refresh the UI. This will ensure that the City dropdown list will get refreshed on changing the country dropdown.
Similarly, we have another dropdown list to display cities data corresponding to each country. On the “onchange” event of the Cities dropdown, we are setting the value of the “cityName” property to the selected city.
We are also displaying the selected country name and city name value on the webpage.
The @functions section contains all our properties and methods. We have defined two variables: countryList of type Country, and cityList of type City. These handle the countries and cities data, respectively. We have also declared three properties to handle the countryId, countryName, and cityName data.
Inside the “OnInitAsync” method, we are calling the GetCountryList web API method to populate countryList. This variable is used to bind the data to the Country dropdown list on page load.
Adding the Link to the Navigation menu
The last step is to add the link to our “CountryData” page in the navigation menu. Open the “BlazorDDL.Client/Shared/NavMenu.cshtml” page and put the following code into it.
<div class="top-row pl-4 navbar navbar-dark"> <a class="navbar-brand" href="/">BlazorDDL</a> <button class="navbar-toggler" onclick=@ToggleNavMenu> <span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span> </button></div><div class=@(collapseNavMenu ? "collapse" : null) onclick=@ToggleNavMenu> <ul class="nav flex-column"> <li class="nav-item px-3"> <NavLink class="nav-link" href="/" Match=NavLinkMatch.All> <span class="oi oi-home" aria-hidden="true"></span> Home </NavLink> </li> <li class="nav-item px-3"> <NavLink class="nav-link" href="/counter"> <span class="oi oi-plus" aria-hidden="true"></span> Counter </NavLink> </li> <li class="nav-item px-3"> <NavLink class="nav-link" href="/fetchdata"> <span class="oi oi-list-rich" aria-hidden="true"></span> Fetch data </NavLink> </li> <li class="nav-item px-3"> <NavLink class="nav-link" href="/country"> <span class="oi oi-list-rich" aria-hidden="true"></span> Country </NavLink> </li> </ul></div>@functions {bool collapseNavMenu = true;void ToggleNavMenu(){ collapseNavMenu = !collapseNavMenu;}}Now we have completed our cascading dropdown list application.
Execution Demo
Launch the application.
A web page will open as shown in the image below. The navigation menu on the left shows the navigation link for the CountryData page.
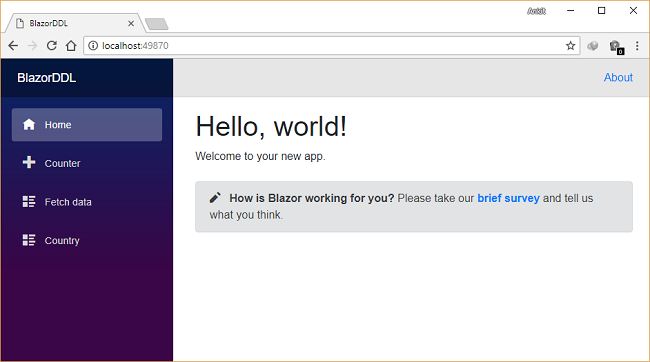
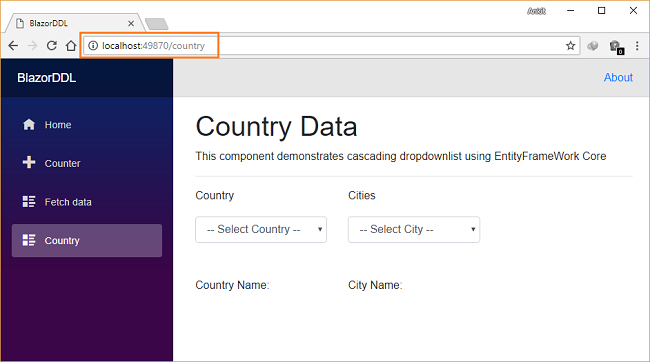
Click on “country” in the navigation menu. It will redirect to the CountryData view where you can see two dropdown s— Country and Cities — on the page. Notice the URL has “/country ” appended to it as we have defined it using the @page directive.
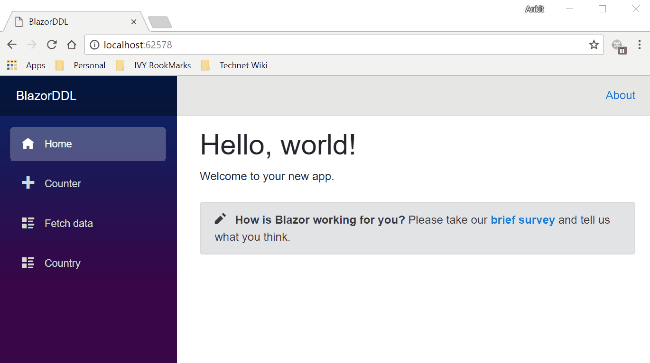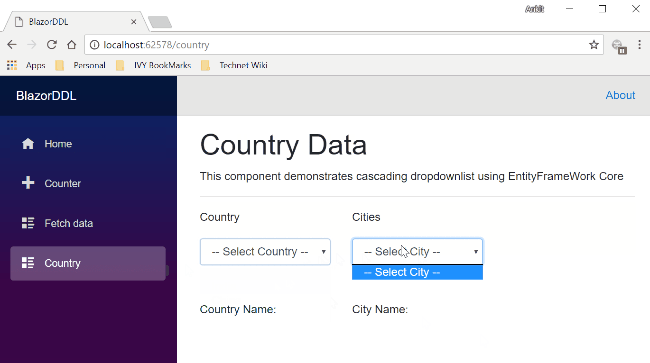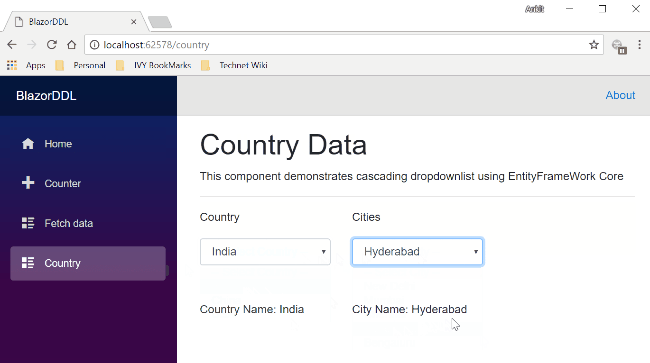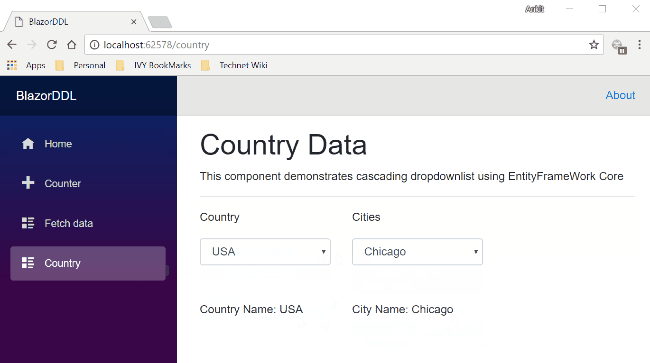
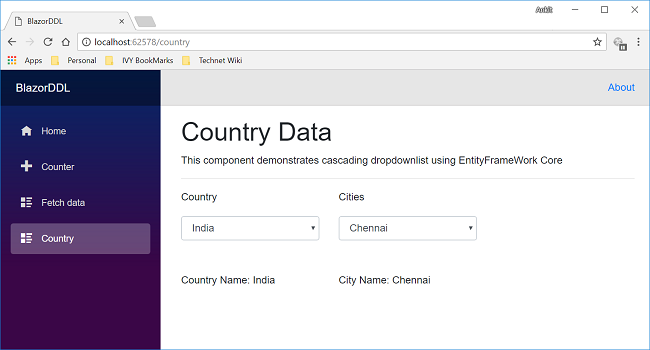
Here you can see both the dropdown lists. The Country dropdown list is already populated with the country data. If we select any country name from this dropdown, then the city dropdown will also get populated with the corresponding city data. We can also see the selected country and city values in the labels below both drop down lists.
Hosting the application
To learn how to host a Blazor application using IIS , refer to Deploying a Blazor Application on IIS
Conclusion
We have learned how to create cascading dropdown lists in Blazor using Entity Framework Core database first approach with the help of Visual Studio 2017 and SQL Server 2014. Please get the source code from GitHub and play around to get a better understanding.
Get my book Blazor Quick Start Guide to learn more about Blazor.
You can check my other articles on Blazor here
You can also find this article at C# Corner.
See Also
- ASP.NET Core — Getting Started With Blazor
- ASP.NET Core — CRUD Using Blazor And Entity Framework Core
- ASP.NET Core — CRUD Using Angular 5 And Entity Framework Core
- ASP.NET Core — CRUD With React.js And Entity Framework Core
- ASP.NET Core — Using Highcharts With Angular 5
Originally published at https://ankitsharmablogs.com/

