Microsoft has recently announced the release of a new .NET web framework called Blazor. In this article, we are going to create a web application using Blazor with the help of Entity Framework Core. We will be creating a sample Employee Record Management System and perform CRUD operations on it.
Prerequisites
- Install .NET Core 2.1 Preview 2 SDK from here
- Install a preview of Visual Studio 2017 v15.7 from here
- Install ASP.NET Core Blazor Language Services extension from here
- SQL Server 2012 or above
The Blazor framework is not supported by versions below Visual Studio 2017 v15.7.
Before proceeding further, I suggest you read my previous article on getting started with Blazor.
Source code
Also, I would recommend that you get the source code from Github before getting started.
Creating the table
We will be using a DB table to store all the records of the employees.
Open SQL Server and use the following script to create the tblEmployee table:
Create table tblEmployee( EmployeeId int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, Name varchar(20) NOT NULL, City varchar(20) NOT NULL, Department varchar(20) NOT NULL, Gender varchar(6) NOT NULL )Now, let’s move on to create our web application.
Create the Blazor web application
Open Visual Studio and select File >> New >> Project.
After selecting the project, a “New Project” dialog will open. Select .NET Core inside Visual C# menu from the left panel.
Then, select “ASP.NET Core Web Application” from the available project types. Put the name of the project as BlazorCrud and press OK.
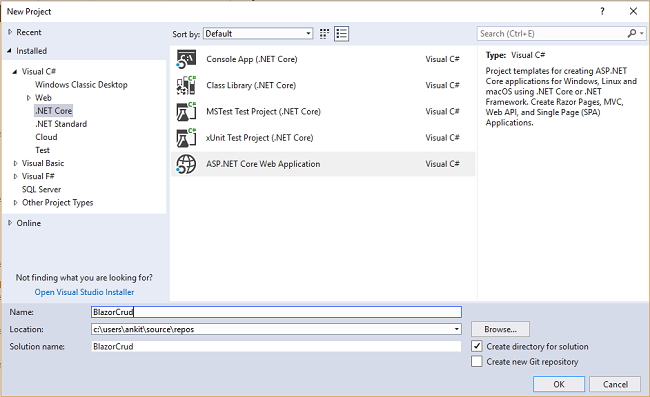
After clicking OK, a new dialog will open asking you to select the project template. You will see two drop-down menus at the top left of the template window. Select “.NET Core” and “ASP.NET Core 2.0” from these dropdowns. Then, select “Blazor (ASP .NET Core hosted)” template and press OK.
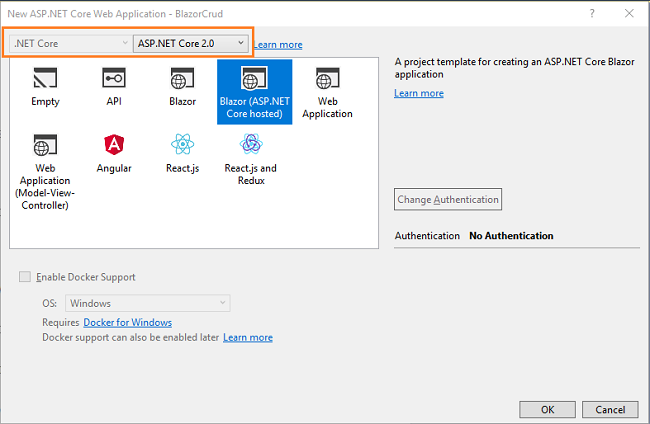
Now, our Blazor solution will be created. You can observe the folder structure in Solution Explorer as shown in the below image.
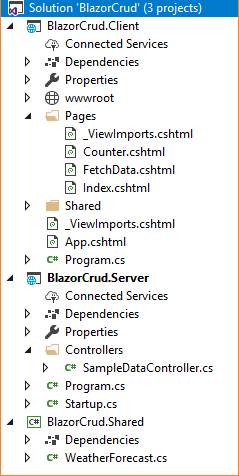
You will see that we have 3 project files created inside this solution:
- BlazorCrud.Client — It has the client side code and contains the pages that will be rendered on the browser.
- BlazorCrud.Server — It has the server side code, such as DB related operations and the web API.
- BlazorCrud.Shared — It contains the shared code that can be accessed by both client and server.
Execute the program. It will open the browser and you will see a page similar to the one shown below.
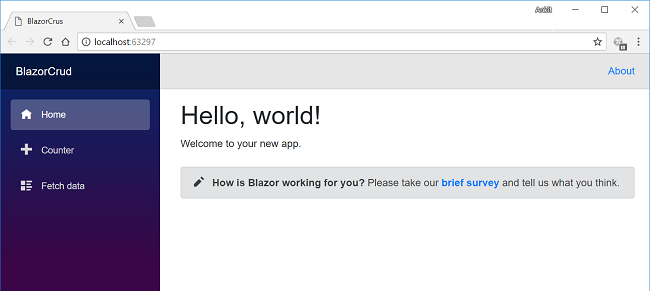
Here you can see a navigation menu on the left side, which contains the navigation to the pages in our application. By default, we have “Counter” and “Fetch Data” pages provided in our application. These default pages will not affect our application, but for the sake of this tutorial, we will delete the fetchdata and counter pages from BlazorCrud.Client/Pages folder.
Adding the model to the application
Right click on BlazorCrud.Shared project and then select Add >> New Folder and name the folder Models. We will be adding our model class in this folder only.
Right click on the Models folder and select Add >> Class. Name your class Employee.cs. This class will contain our Employee model properties. Now our BlazorCrud.Shared project has the following structure:

Open Employee.cs and put the following code in it:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; using System.Text; namespace BlazorCrud.Shared.Models { public class Employee { public int EmployeeId { get; set; } [Required] public string Name { get; set; } [Required] public string Gender { get; set; } [Required] public string Department { get; set; } [Required] public string City { get; set; } } }And so our model has been created. Now we will create our data access layer.
Creating the data access layer for the application
Right click on BlazorCrud.Server project and then select Add >> New Folder and name the folder DataAccess. We will be adding our classes to handle database-related operations inside this folder only.
Right click on the DataAccess folder and select Add >> Class. Name your class EmployeeContext.cs. This is our Entity Framework DB context class that allows us to interact with the database. Open EmployeeContext.cs and put the following code into it:
using BlazorCrud.Shared.Models; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace BlazorCrud.Server.DataAccess { public class EmployeeContext : DbContext { public virtual DbSet<Employee> tblEmployee { get; set; } protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) { if (!optionsBuilder.IsConfigured) { optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(@"Put Your Connection string here"); } } } }Do not forget to put in your own connection string.
Add one more class to DataAccess folder and name it EmployeeDataAccessLayer.cs. This class will handle our CRUD related DB operations. Open EmployeeDataAccessLayer.cs and put the following code into it:
using BlazorCrud.Shared.Models; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace BlazorCrud.Server.DataAccess { public class EmployeeDataAccessLayer { EmployeeContext db = new EmployeeContext(); //To Get all employees details public IEnumerable<Employee> GetAllEmployees() { try { return db.tblEmployee.ToList(); } catch { throw; } } //To Add new employee record public void AddEmployee(Employee employee) { try { db.tblEmployee.Add(employee); db.SaveChanges(); } catch { throw; } } //To Update the records of a particluar employee public void UpdateEmployee(Employee employee) { try { db.Entry(employee).State = EntityState.Modified; db.SaveChanges(); } catch { throw; } } //Get the details of a particular employee public Employee GetEmployeeData(int id) { try { Employee employee = db.tblEmployee.Find(id); return employee; } catch { throw; } } //To Delete the record of a particular employee public void DeleteEmployee(int id) { try { Employee emp = db.tblEmployee.Find(id); db.tblEmployee.Remove(emp); db.SaveChanges(); } catch { throw; } } } }Now our data access layer is complete. Next, we will proceed to create our web API Controller.
Adding the web API controller to the application
Right click on BlazorCrud.Server/Controllers folder and select Add >> New Item. An “Add New Item” dialog box will open. Select ASP.NET from the left panel, then select “API Controller Class” from the templates panel and name it EmployeeController.cs. Press OK.
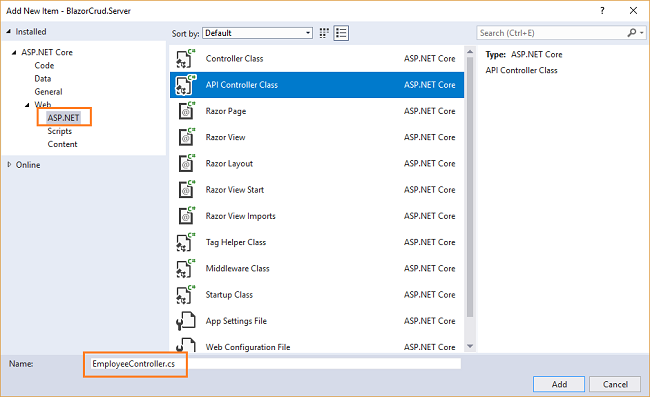
This will create our API EmployeeController class.
We will call the methods of the EmployeeDataAccessLayer class to fetch data and pass on the data to the client side.
Open the EmployeeController.cs file and put the following code into it:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using BlazorCrud.Server.DataAccess; using BlazorCrud.Shared.Models; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; namespace BlazorCrud.Server.Controllers { public class EmployeeController : Controller { EmployeeDataAccessLayer objemployee = new EmployeeDataAccessLayer(); [HttpGet] [Route("api/Employee/Index")] public IEnumerable<Employee> Index() { return objemployee.GetAllEmployees(); } [HttpPost] [Route("api/Employee/Create")] public void Create([FromBody] Employee employee) { if (ModelState.IsValid) objemployee.AddEmployee(employee); } [HttpGet] [Route("api/Employee/Details/{id}")] public Employee Details(int id) { return objemployee.GetEmployeeData(id); } [HttpPut] [Route("api/Employee/Edit")] public void Edit([FromBody]Employee employee) { if (ModelState.IsValid) objemployee.UpdateEmployee(employee); } [HttpDelete] [Route("api/Employee/Delete/{id}")] public void Delete(int id) { objemployee.DeleteEmployee(id); } } }At this point, our BlazorCrud.Server project has the following structure:
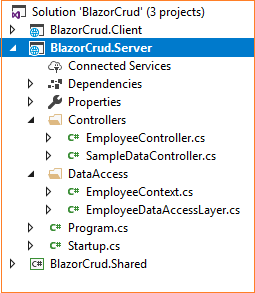
We are done with our backend logic. So we will now proceed to code our client side.
Adding Razor View to the application
Right click on the BlazorCrud.Client/Pages folder and then select Add >> New Item. An “Add New Item” dialog box will open, select Web from the left panel, then select “Razor View” from the templates panel and name it FetchEmployee.cshtml.
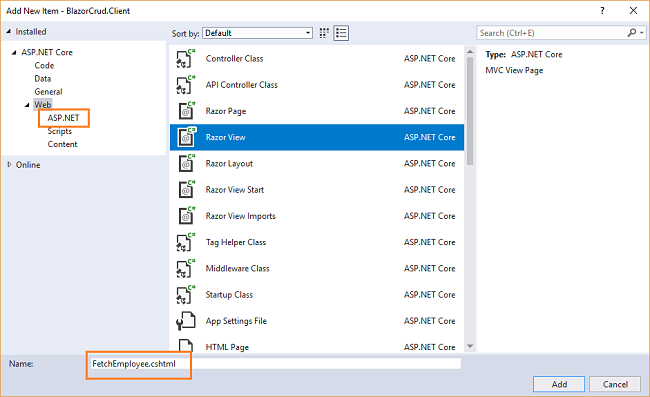
This will add a FetchEmployee.cshtml page to our BlazorCrud.Client/Pages folder. Similarly, add 3 more pages: AddEmployee.cshtml, EditEmployee.cshtml, and DeleteEmployee.cshtml.
Now our BlazorCrud.Client project has the following structure:
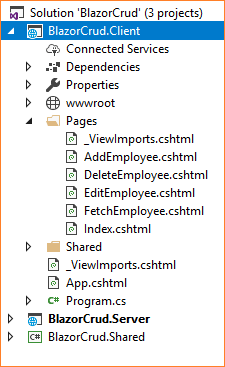
Let’s add code to these pages.
FetchEmployee.cshtml
This page will display all the employee records present in the database. Additionally, we will also provide the action methods Edit and Delete on each record.
Open FetchEmployee.cshtml and put the following code in it:
@using BlazorCrud.Shared.Models@page "/fetchemployee"@inject HttpClient Http<h1>Employee Data</h1><p>This component demonstrates fetching Employee data from the server.</p><p> <a href="/addemployee">Create New</a></p>@if (empList == null){ <p><em>Loading...</em></p>}else{ <table class='table'> <thead> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Gender</th> <th>Department</th> <th>City</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> @foreach (var emp in empList) { <tr> <td>@emp.EmployeeId</td> <td>@emp.Name</td> <td>@emp.Gender</td> <td>@emp.Department</td> <td>@emp.City</td> <td> <a href='/editemployee/@emp.EmployeeId'>Edit</a> | <a href='/delete/@emp.EmployeeId'>Delete</a> </td> </tr> } </tbody> </table>}@functions {Employee[] empList;protected override async Task OnInitAsync(){ empList = await Http.GetJsonAsync<Employee[]> ("/api/Employee/Index");}}Let’s understand this code. At the top, we have included the BlazorEFApp.Shared.Models namespace so that we can use our Employee model class in this page.
We are defining the route of this page using the @page directive. So, in this application, if we append “/fetchemployee” to the base URL, we will be redirected to this page. We are also injecting HttpClient service to enable the web API call.
Then we have defined the HTML part to display all the employees records in a tabular manner. We have also added two action links for Edit and Delete which will navigate to the EditEmployee.cshtml and DeleteEmployee.cshtml pages, respectively.
At the bottom of the page, we have a @functions section which contains our business logic. We have created an array variable empList of type Employee, and we and populate it inside OnInitAsync method by calling our web API. This will bind to our HTML table on the page load.
AddEmployee.cshtml
This page is used to create a new employee record.
Open AddEmployee.cshtml and put the following code into it:
@using BlazorCrud.Shared.Models@page "/addemployee"@inject HttpClient Http@inject Microsoft.AspNetCore.Blazor.Services.IUriHelper UriHelper<h1>Create</h1><h3>Employee</h3><hr /><div class="row"> <div class="col-md-4"> <form> <div class="form-group"> <label for="Name" class="control-label">Name</label> <input for="Name" class="form-control" bind="@emp.Name" /> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label asp-for="Gender" class="control-label">Gender</label> <select asp-for="Gender" class="form-control" bind="@emp.Gender"> <option value="">-- Select Gender --</option> <option value="Male">Male</option> <option value="Female">Female</option> </select> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label asp-for="Department" class="control-label">Department</label> <input asp-for="Department" class="form-control" bind="@emp.Department" /> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label asp-for="City" class="control-label">City</label> <input asp-for="City" class="form-control" bind="@emp.City" /> </div> <div class="form-group"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-default" onclick="@(async () => await CreateEmployee())">Save</button> <button class="btn" onclick="@cancel">Cancel</button> </div> </form> </div></div>@functions {Employee emp = new Employee();protected async Task CreateEmployee(){ await Http.SendJsonAsync(HttpMethod.Post, "/api/Employee/Create", emp); UriHelper.NavigateTo("/fetchemployee");}void cancel(){ UriHelper.NavigateTo("/fetchemployee");}}In this page the route is “/addemployee”.
We are also injecting the “Microsoft.AspNetCore.Blazor.Services.IUriHelper” service to enable URL redirection. The HTML part will generate a form to get input from the user. The attribute “bind” is used to bind the value entered in the textbox to the properties of the Employee object.
In the @functions section, we have defined two methods. The method CreateEmployee will be invoked on clicking the “Submit” button and will send a POST request to our API along with the Employee object emp.
The Cancel method will be invoked on clicking the cancel button and will redirect the user back to the FetchEmployee page.
EditEmployee.cshtml
This page is used to edit the details of an employee.
Open EditEmployee.cshtml and put the following code into it:
@using BlazorCrud.Shared.Models@page "/editemployee/{empID}"@inject HttpClient Http@inject Microsoft.AspNetCore.Blazor.Services.IUriHelper UriHelper<h2>Edit</h2><h4>Employees</h4><hr /><div class="row"> <div class="col-md-4"> <form> <div class="form-group"> <label for="Name" class="control-label">Name</label> <input for="Name" class="form-control" bind="@emp.Name" /> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label asp-for="Gender" class="control-label">Gender</label> <select asp-for="Gender" class="form-control" bind="@emp.Gender"> <option value="">-- Select Gender --</option> <option value="Male">Male</option> <option value="Female">Female</option> </select> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label asp-for="Department" class="control-label">Department</label> <input asp-for="Department" class="form-control" bind="@emp.Department" /> </div> <div class=" form-group"> <label asp-for="City" class="control-label">City</label> <input asp-for="City" class="form-control" bind="@emp.City" /> </div> <div class="form-group"> <input type="submit" value="Save" onclick="@(async () => await UpdateEmployee())" class="btn btn-default" /> <input type="submit" value="Cancel" onclick="@cancel" class="btn" /> </div> </form> </div></div>@functions {[Parameter]string empID { get; set; }Employee emp = new Employee();protected override async Task OnInitAsync(){ emp = await Http.GetJsonAsync<Employee>("/api/Employee/Details/" + Convert.ToInt32(empID));}protected async Task UpdateEmployee(){ await Http.SendJsonAsync(HttpMethod.Put, "api/Employee/Edit", emp); UriHelper.NavigateTo("/fetchemployee");}void cancel(){ UriHelper.NavigateTo("/fetchemployee");}}In this page we have defined the route as “/editemployee/{empID}”. empID is an URL parameter of type string declared in the @functions section. We will use the [Parameter] attribute to mark the variable as a parameter. To navigate to this page, we need to pass the employee id in the URL which will be captured in the empID variable.
If we do not mark the variable with the [Parameter] attribute, we will get the following error: “Object of type ‘BlazorCrud.Client.Pages.EditEmployee’ has a property matching the name ’empID’, but it does not have [ParameterAttribute] applied.” This will not allow empID to bind to the employee id value passed in the parameter.
The HTML part is similar to that of the AddEmployee.cshtml page. The attribute “bind” is used for two-way binding, that is binding the textbox values to employee object properties, and vice versa.
Inside the @functions section, we are fetching the employee records in the OnInitAsync method based on the employeeID passed in the parameter. This will bind to the fields in the form on page load itself.
The UpdateEmployee method will send a PUT request to our API along with the Employee object emp. The Cancel method will be invoked on clicking the cancel button and will redirect the user back to the FetchEmployee page.
DeleteEmployee.cshtml
This page will be used to delete an employee record.
Open DeleteEmployee.cshtml and put the following code into it:
@using BlazorCrud.Shared.Models@page "/delete/{empID}"@inject HttpClient Http@inject Microsoft.AspNetCore.Blazor.Services.IUriHelper UriHelper<h2>Delete</h2><h3>Are you sure you want to delete employee with id : @empID</h3><br /><div class="col-md-4"> <table class="table"> <tr> <td>Name</td> <td>@emp.Name</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Gender</td> <td>@emp.Gender</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Department</td> <td>@emp.Department</td> </tr> <tr> <td>City</td> <td>@emp.City</td> </tr> </table> <div class="form-group"> <input type="submit" value="Delete" onclick="@(async () => await Delete())" class="btn btn-default" /> <input type="submit" value="Cancel" onclick="@cancel" class="btn" /> </div></div>@functions {[Parameter]string empID { get; set; }Employee emp = new Employee();protected override async Task OnInitAsync(){ emp = await Http.GetJsonAsync<Employee> ("/api/Employee/Details/" + Convert.ToInt32(empID));}protected async Task Delete(){ await Http.DeleteAsync("api/Employee/Delete/" + Convert.ToInt32(empID)); UriHelper.NavigateTo("/fetchemployee");}void cancel(){ UriHelper.NavigateTo("/fetchemployee");}}The route for this page is also parameterized, since we are fetching the record of the employee on page load.
The HTML part will display the employee data and ask the user for confirmation to delete the employee record.
Inside the @functions section, we are fetching the employee records inthe OnInitAsync method based on the employeeID passed in the parameter. This will display the employee records as the page loads.
The Delete method will be invoked on clicking the “Delete” button, which will send a delete request to our API along with the employee ID of the employee to be deleted. On successful deletion, the user will be navigated back to the FetchEmployee page.
Adding a link to the Navigation menu
The last step is to define the navigation menu for our application. Open the BlazorCrud.Client/Shared/ NavMenu.cshtml file and put the following code in it:
<div class="top-row pl-4 navbar navbar-dark"> <a class="navbar-brand" href="/">BlazorCrud</a> <button class="navbar-toggler" onclick=@ToggleNavMenu> <span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span> </button></div><div class=@(collapseNavMenu ? "collapse" : null) onclick=@ToggleNavMenu> <ul class="nav flex-column"> <li class="nav-item px-3"> <NavLink class="nav-link" href="/" Match=NavLinkMatch.All> <span class="oi oi-home" aria-hidden="true"></span> Home </NavLink> </li> <li class="nav-item px-3"> <NavLink class="nav-link" href="/fetchemployee"> <span class="oi oi-list-rich" aria-hidden="true"></span> Fetch employee </NavLink> </li> </ul></div>@functions {bool collapseNavMenu = true;void ToggleNavMenu(){ collapseNavMenu = !collapseNavMenu;}}And that’s it. We have created our first ASP.NET Core application using Blazor and Entity Framework Core.
Execution demo
Launch the application.
A web page will open as shown in the image below. The navigation menu on the left will show the navigation link for the Home and Fetch Employee pages.
Click on Fetch employee in the navigation menu. It will redirect to the FetchEmployee view and will display all the employee data on the page. Notice that the URL has “/fetchemployee” appended to it, as we have defined it using the @page directive.
Since we have not added any data, it is empty.
Click on CreateNew to navigate to AddEmployee view. Notice the URL has “/addemployee” appended to it, as we have defined it using the @page directive. Add a new Employee record as shown in the image below:
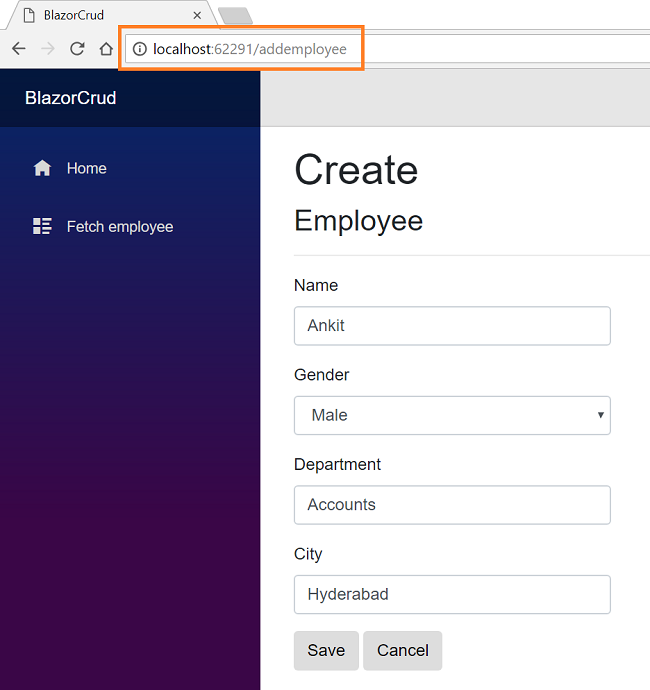
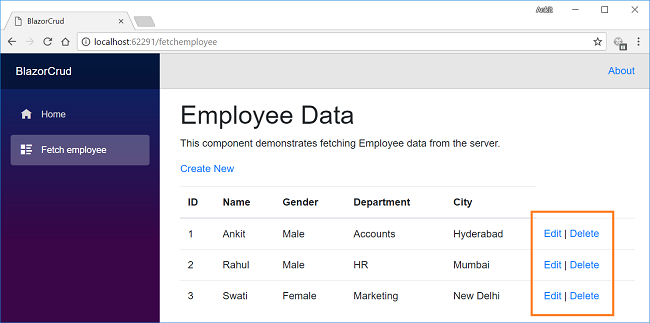
After inserting data in all the fields, click on the “Save” button. The new employee record will be created, and you will be redirected to the FetchEmployee view, which will display records of all the employees. Here, we can also see the action methods Edit and Delete corresponding to each record.
If we want to edit an existing employee record, we just click on the Edit action link. It will open the Edit view as shown below. Here we can change the employee data. Notice that we have passed the employee id in the URL parameter.
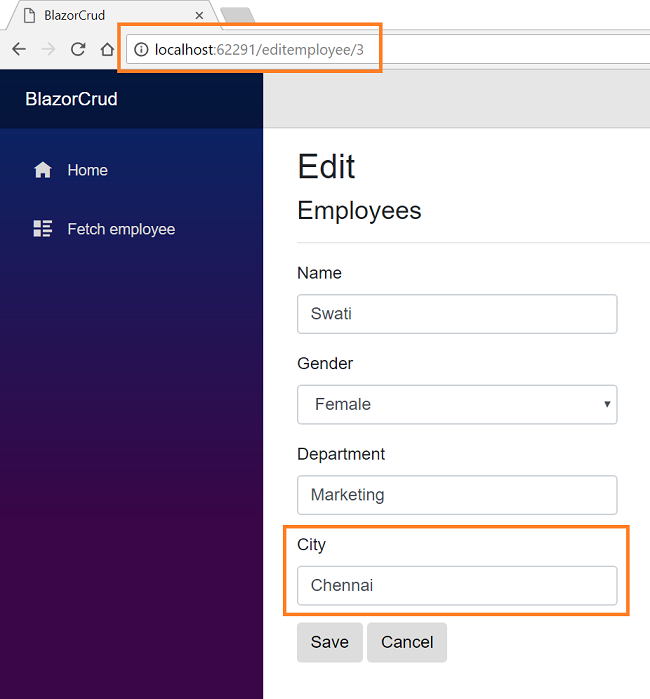
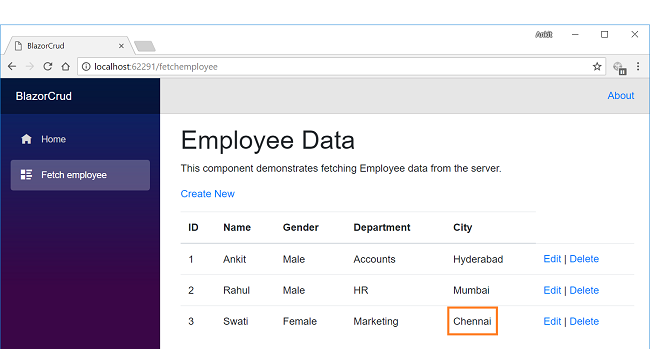
Here we have changed the City of employee Swati from New Delhi to Chennai. Click on “Save” to return to the FetchEmployee view to see the updated changes as highlighted in the image below:
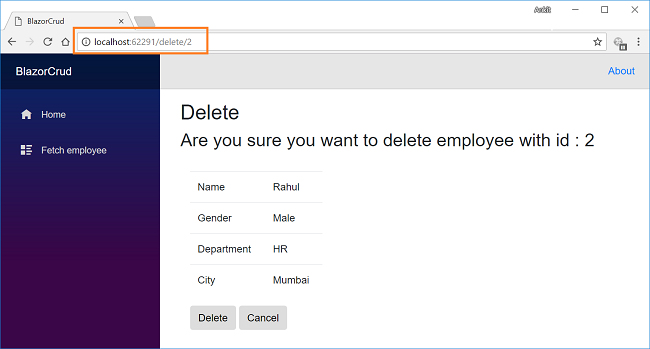
Now, we will perform the Delete operation on the employee named Rahul. Click on the Delete action link which will open the Delete view asking for a confirmation to delete. Notice that we have passed the employee id in the URL parameter.
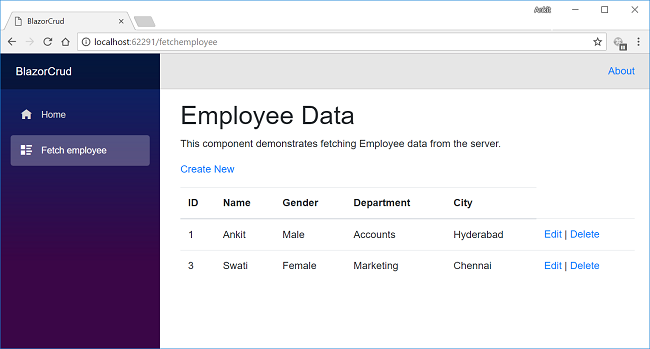
Once we click on the Delete button, it will delete the employee record and we will be redirected to the FetchEmployee view. Here, we can see that the employee with name Rahul has been removed from our record.
Hosting the application
To learn how to host a Blazor application using IIS, refer to Deploying a Blazor Application on IIS.
See Also
- ASP.NET Core — CRUD Using Angular 5 And Entity Framework Core
- CRUD Operations With ASP.NET Core Using Angular 5 and ADO.NET
- Getting Started With Angular 5 Using Visual Studio Code
- CRUD Operation With ASP.NET Core MVC Using Visual Studio Code and EF
- CRUD Operation With ASP.NET Core MVC Using ADO.NET and Visual Studio 2017
- CRUD Operation With ASP.NET Core MVC using Visual Studio Code and ADO.NET
Conclusion
We have created an ASP.NET Core application using the new web framework Blazor and Entity Framework Core with the help of Visual Studio 2017 and SQL Server 2012. We have also performed CRUD operations on our application.
You can also fork this application on Github. Try this new framework and let me know what you think of it in the comments section below.
Get my book Blazor Quick Start Guide to learn more about Blazor.
You can also find this article at C# Corner.
You can check my other articles on ASP .NET Core here
Originally published at https://ankitsharmablogs.com/

