? Local Tile Server for Geospatial Rasters
Need to visualize a rather large (gigabytes) raster you have locally? This is for you.
A Flask application for serving tiles from large raster files in
the Slippy Maps standard
(i.e., /zoom/x/y.png)
? Highlights
- Create a local tile server for large geospatial images
- View local or remote* raster files with
ipyleafletorfolium - Extract regions of interest (ROIs) interactively
- Use the example datasets to generate Digital Elevation Models
- Visualize rasters with the included CesiumJS web viewer
*remote raster files should be pre-tiled Cloud Optimized GeoTiffs
ℹ️ Overview
Under the hood, this uses large_image
to launch a tile server in a background thread which will serve raster imagery
to a tile viewer (see ipyleaflet and folium examples below).
This tile server can efficiently deliver varying levels of detail of your
raster imagery to your viewer; it helps to have pre-tiled, Cloud Optimized
GeoTIFFs (COG), but no wories if not as large_image will tile and cache for
you when opening the raster.
There is an included, standalone web viewer leveraging
CesiumJS and GeoJS.
You can use the web viewer to select and extract regions of interest from rasters.
Disclaimer: I put this together over a weekend and I’m definitely going to
change a few things moving forward to make it more stable/robust. This means
that things will most likely break between minor releases (I use the
major.minor.patch versioning scheme).
⬇️ Installation
Install from PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/localtileserver/
pip install localtileserver
? A Brief Note on Installing GDAL
GDAL can be a pain in the ? to install, and you may want to handle GDAL
before installing localtileserver.
If on linux, I highly recommend using the large_image_wheels from Kitware.
pip install --find-links=https://girder.github.io/large_image_wheels --no-cache GDAL
Otherwise, I recommend using conda:
conda install -c conda-forge GDAL
? Feedback
Please share your thoughts and questions on the Discussions board.
If you would like to report any bugs or make feature requests, please open an issue.
If filing a bug report, please share a scooby Report:
import localtileserver
print(localtileserver.Report())
? Usage
? ipyleaflet Tile Layers
The TileClient class is a nifty tool to launch a tile server as a background
thread to serve image tiles from any raster file on your local file system.
Additionally, it can be used in conjunction with the get_leaflet_tile_layer
utility to create an ipyleaflet.TileLayer for interactive visualization in
a Jupyter notebook. Here is an example:
from localtileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, TileClient
from ipyleaflet import Map
# First, create a tile server from local raster file
tile_client = TileClient('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif')
# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server
t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client)
# Create ipyleaflet map, add tile layer, and display
m = Map(center=tile_client.center())
m.add_layer(t)
m
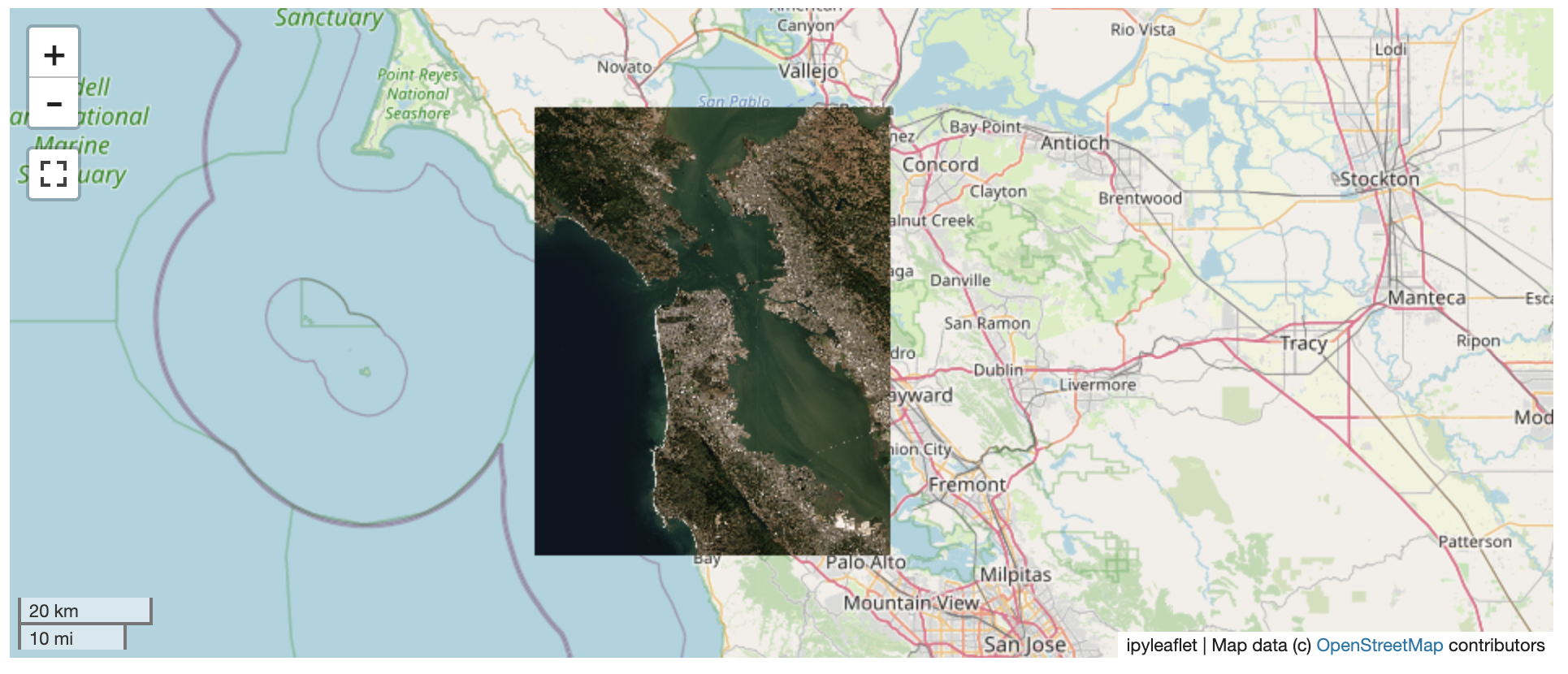
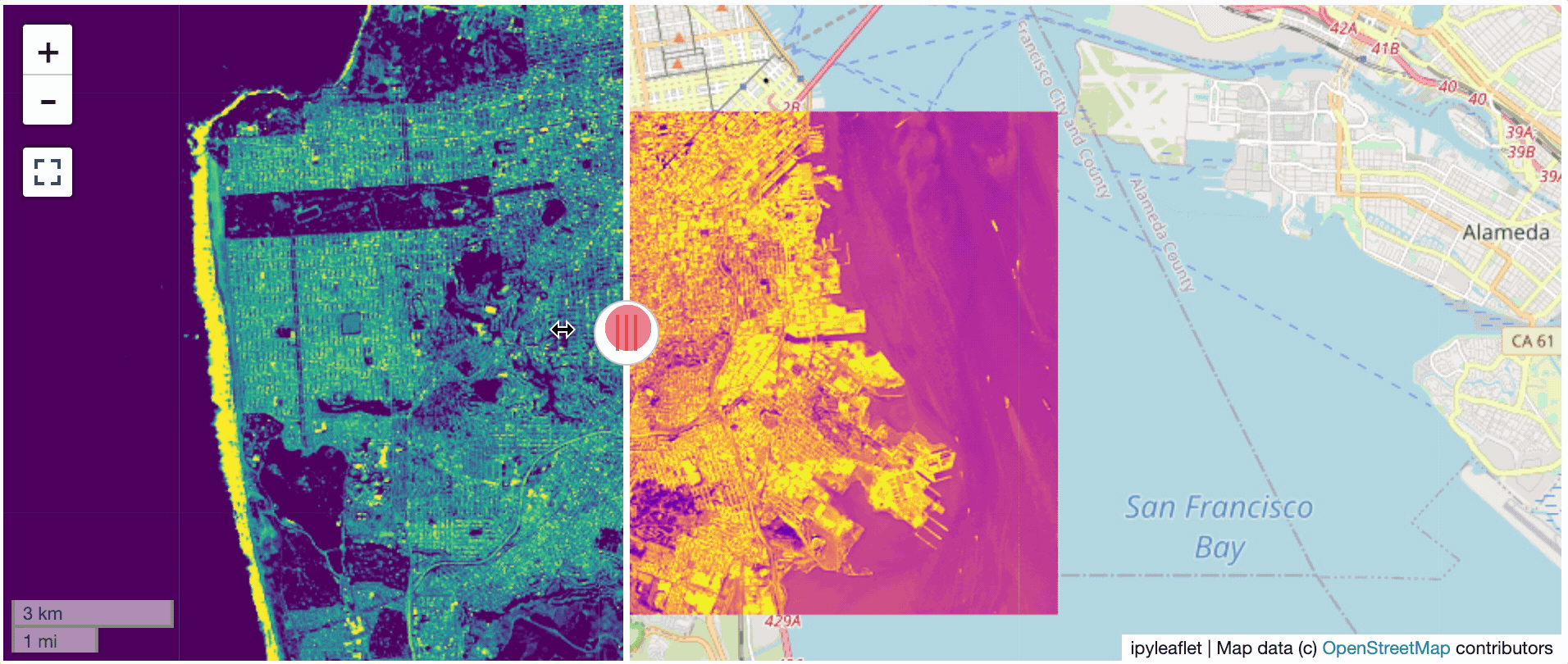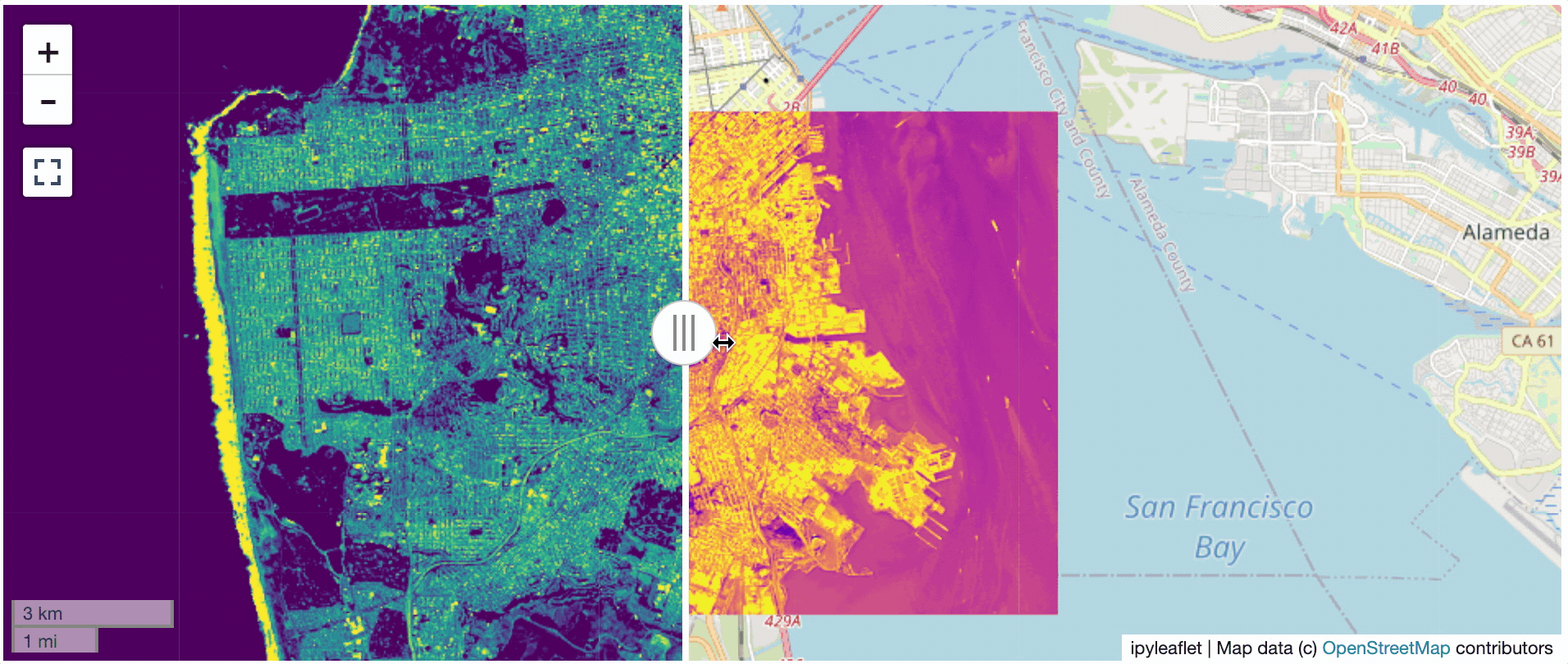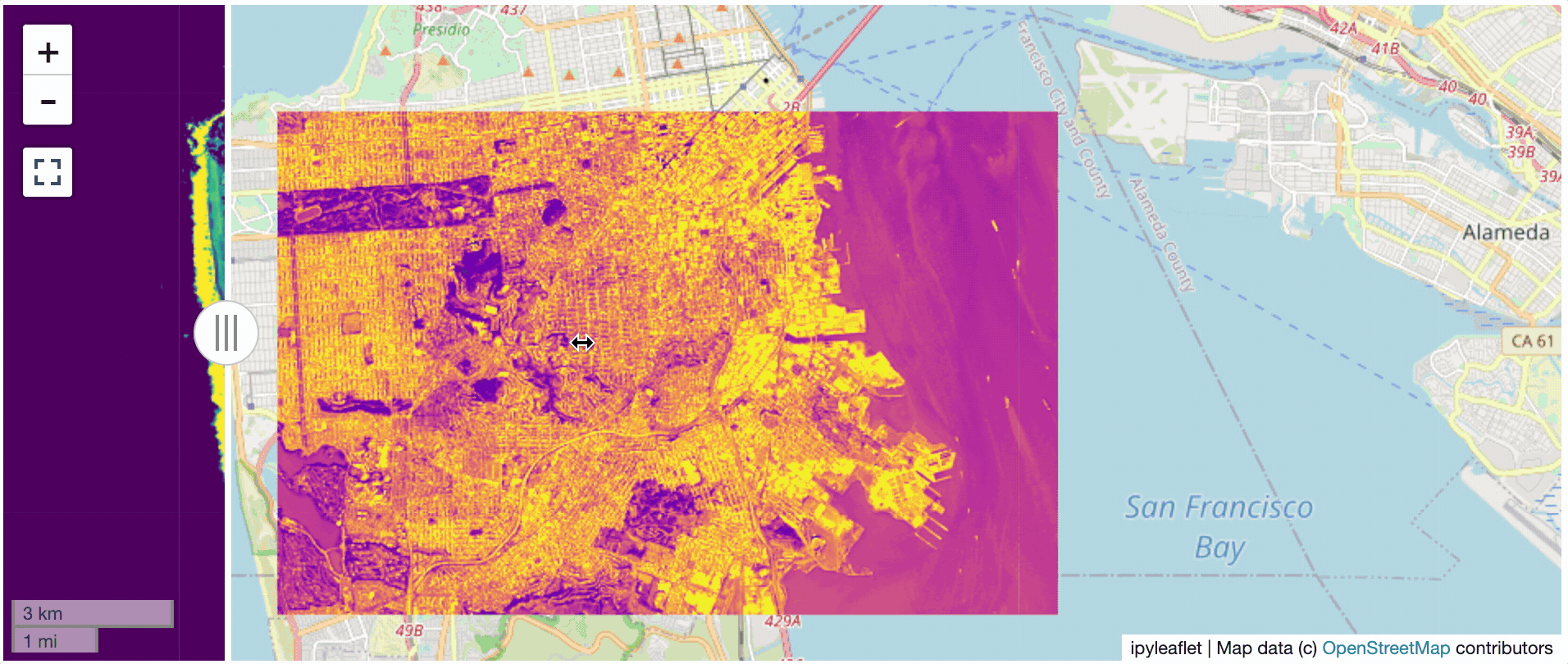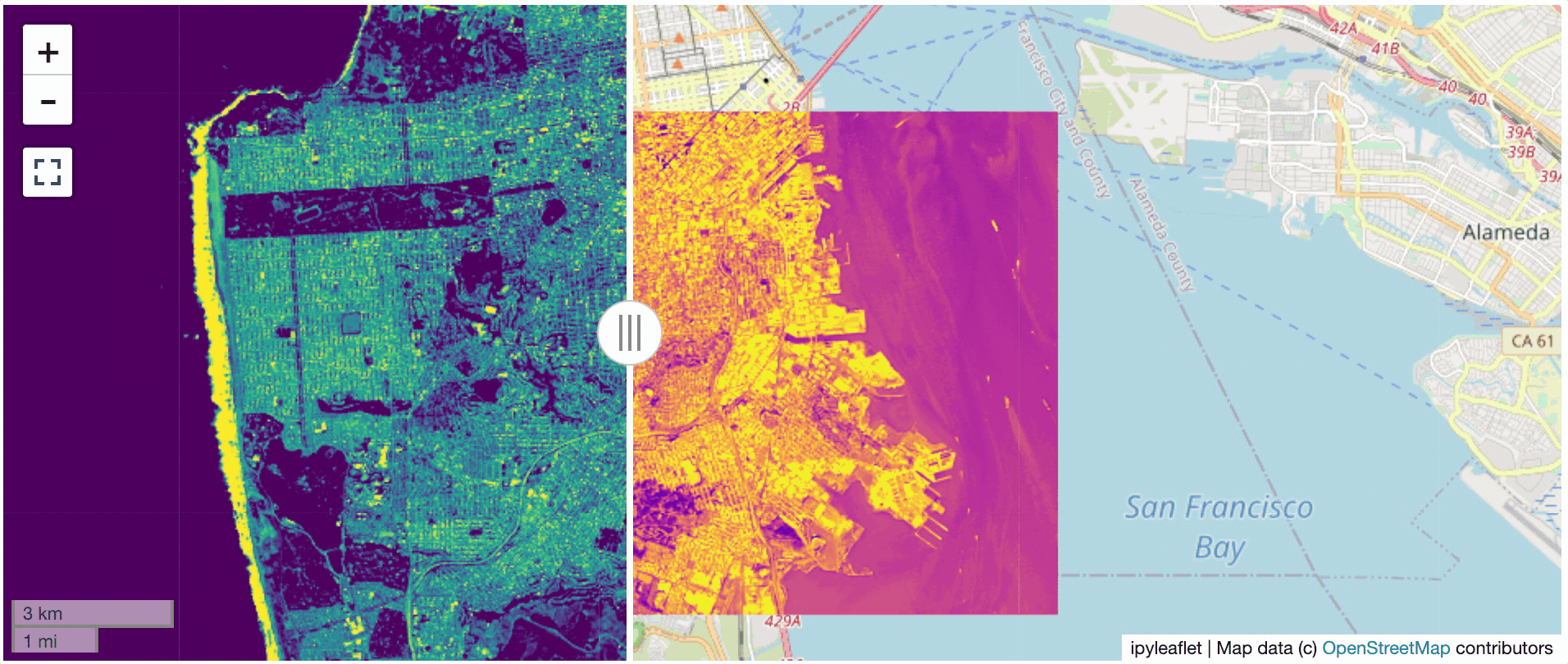
? Two Rasters at Once
from localtileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer
from ipyleaflet import Map, ScaleControl, FullScreenControl, SplitMapControl
# Create 2 tile layers from 2 separate raster files
l = get_leaflet_tile_layer('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif',
band=1, palette='matplotlib.Viridis_20', vmin=50, vmax=200)
r = get_leaflet_tile_layer('~/Desktop/small.tif',
band=2, palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', vmin=0, vmax=150)
# Make the ipyleaflet map
m = Map(center=(37.7249511580583, -122.27230466902257), zoom=9)
control = SplitMapControl(left_layer=l, right_layer=r)
m.add_control(control)
m.add_control(ScaleControl(position='bottomleft'))
m.add_control(FullScreenControl())
m
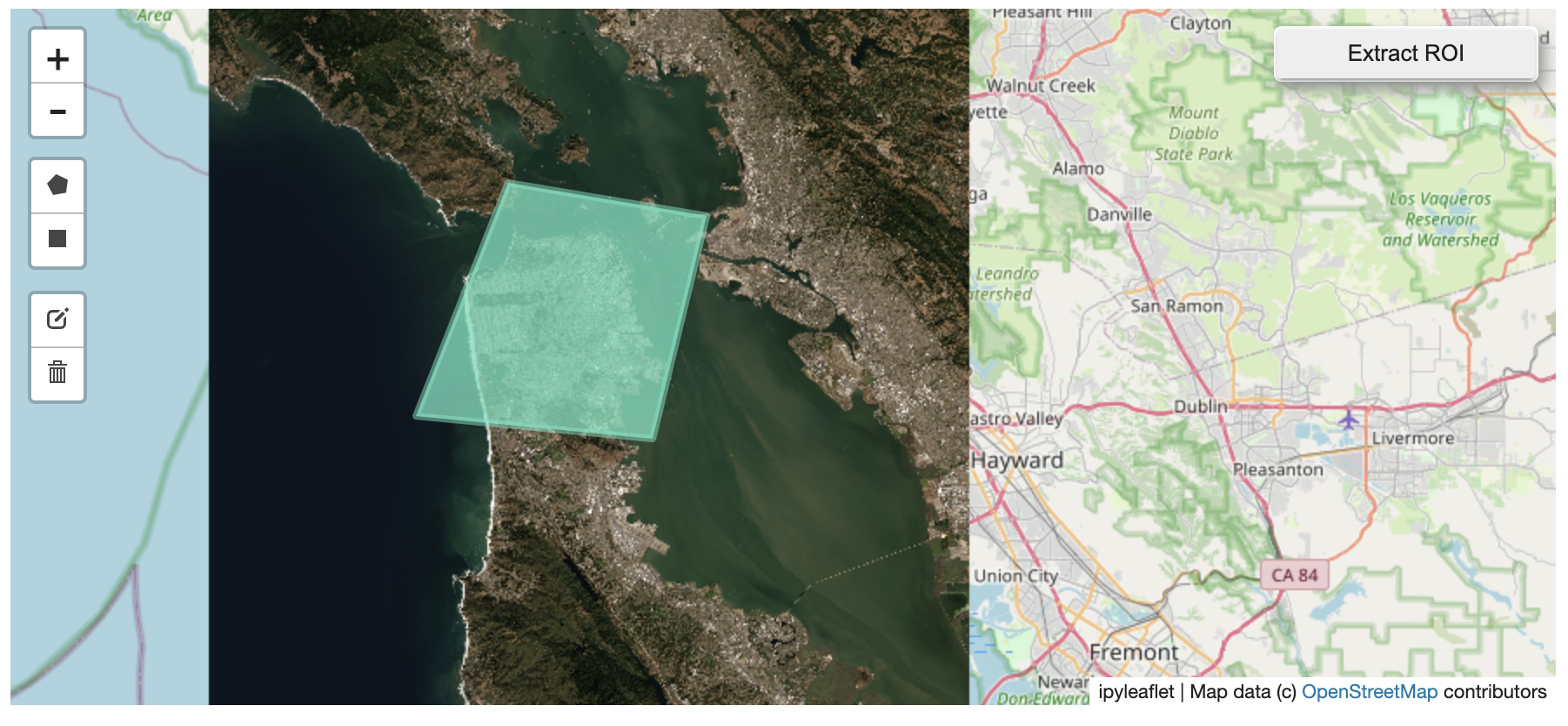
? Using ipyleaflet for ROI Extraction
I have included the get_leaflet_roi_controls utility to create some leaflet
UI controls for extracting regions of interest from a tile client. You can
use it as follows and then draw a polygon and click the “Extract ROI” button.
The outputs are save in your working directory by default (next to the Jupyter notebook).
from localtileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, get_leaflet_roi_controls
from localtileserver import TileClient
from ipyleaflet import Map
# First, create a tile server from local raster file
tile_client = TileClient('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif')
# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server
t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client)
# Create ipyleaflet controls to extract an ROI
draw_control, roi_control = get_leaflet_roi_controls(tile_client)
# Create ipyleaflet map, add layers, add controls, and display
m = Map(center=(37.7249511580583, -122.27230466902257), zoom=9)
m.add_layer(t)
m.add_control(draw_control)
m.add_control(roi_control)
m
? folium Tile Layers
Similarly to the support provided for ipyleaflet, I have included a utility
to generate a folium.TileLayer
with get_folium_tile_layer. Here is an example with almost the exact same
code as the ipyleaflet example, just note that Map is imported from
folium and we use add_child instead of add_layer:
from localtileserver import get_folium_tile_layer
from localtileserver import TileClient
from folium import Map
# First, create a tile server from local raster file
tile_client = TileClient('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif')
# Create folium tile layer from that server
t = get_folium_tile_layer(tile_client)
m = Map(location=tile_client.center())
m.add_child(t)
m
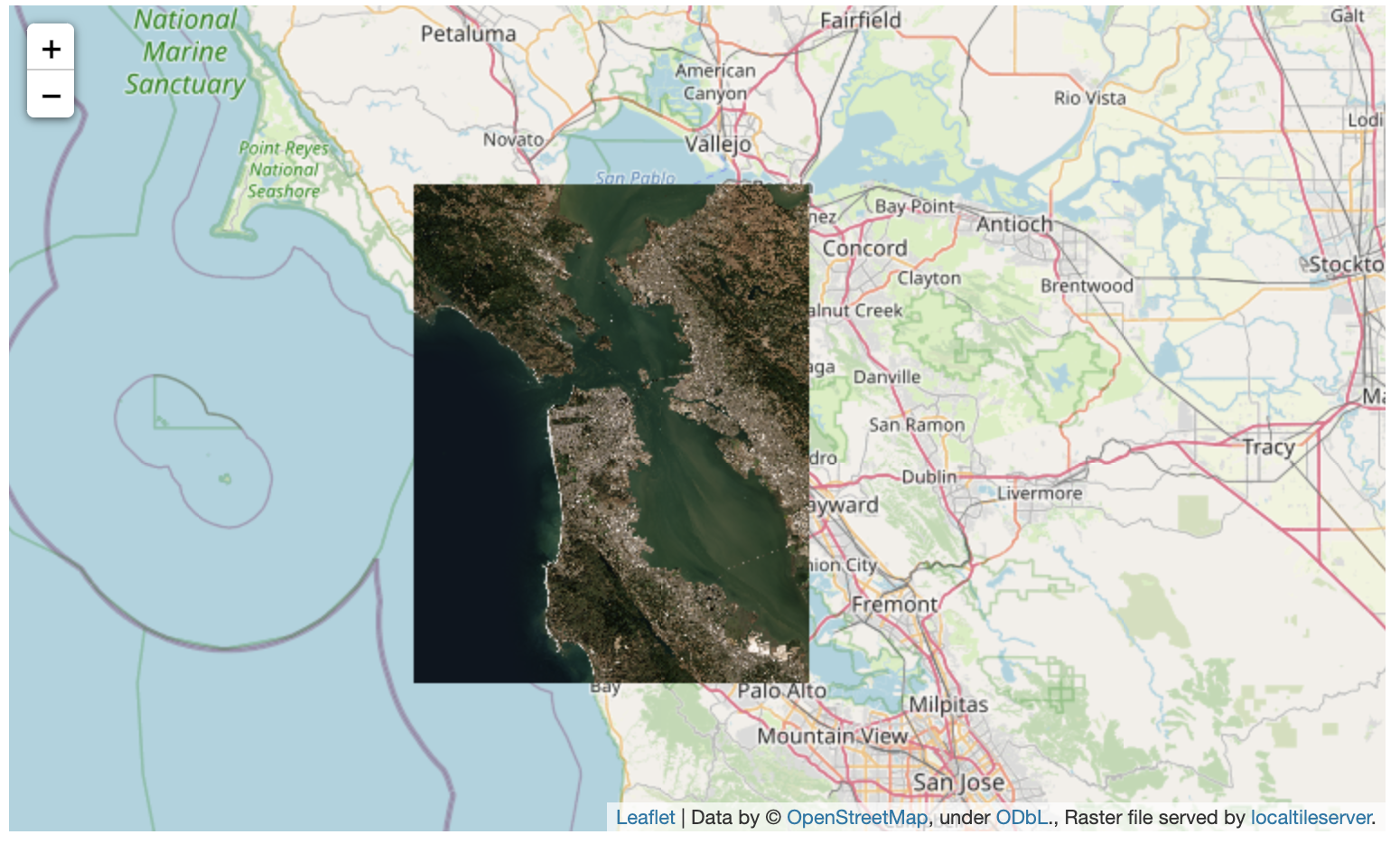
☁️ Remote Cloud Optimized GeoTiffs (COGs)
While localtileserver is intended to be used only with raster files existing
on your local filesystem, there is support for URL files through GDAL’s
Virtual Storage Interface.
Simply pass your http<s>:// or s3:// URL to the TileClient. This will
work quite well for pre-tiled Cloud Optimized GeoTiffs, but I do not recommend
doing this with non-tiled raster formats.
For example, the raster at the url below is ~3GiB but because it is pre-tiled,
we can view tiles of the remote file very efficiently in a Jupyter notebook.
from localtileserver import get_folium_tile_layer
from localtileserver import TileClient
from folium import Map
url = 'https://opendata.digitalglobe.com/events/california-fire-2020/pre-event/2018-02-16/pine-gulch-fire20/1030010076004E00.tif'
# First, create a tile server from local raster file
tile_client = TileClient(url)
# Create folium tile layer from that server
t = get_folium_tile_layer(tile_client)
m = Map(location=tile_client.center())
m.add_child(t)
m
Note that the Virtual Storage Interface is a complex API, and TileClient
currently only handles vsis3 and vsicurl. If you need a different VFS
mechanism, simply create your /vsi path and pass that to TileClient.
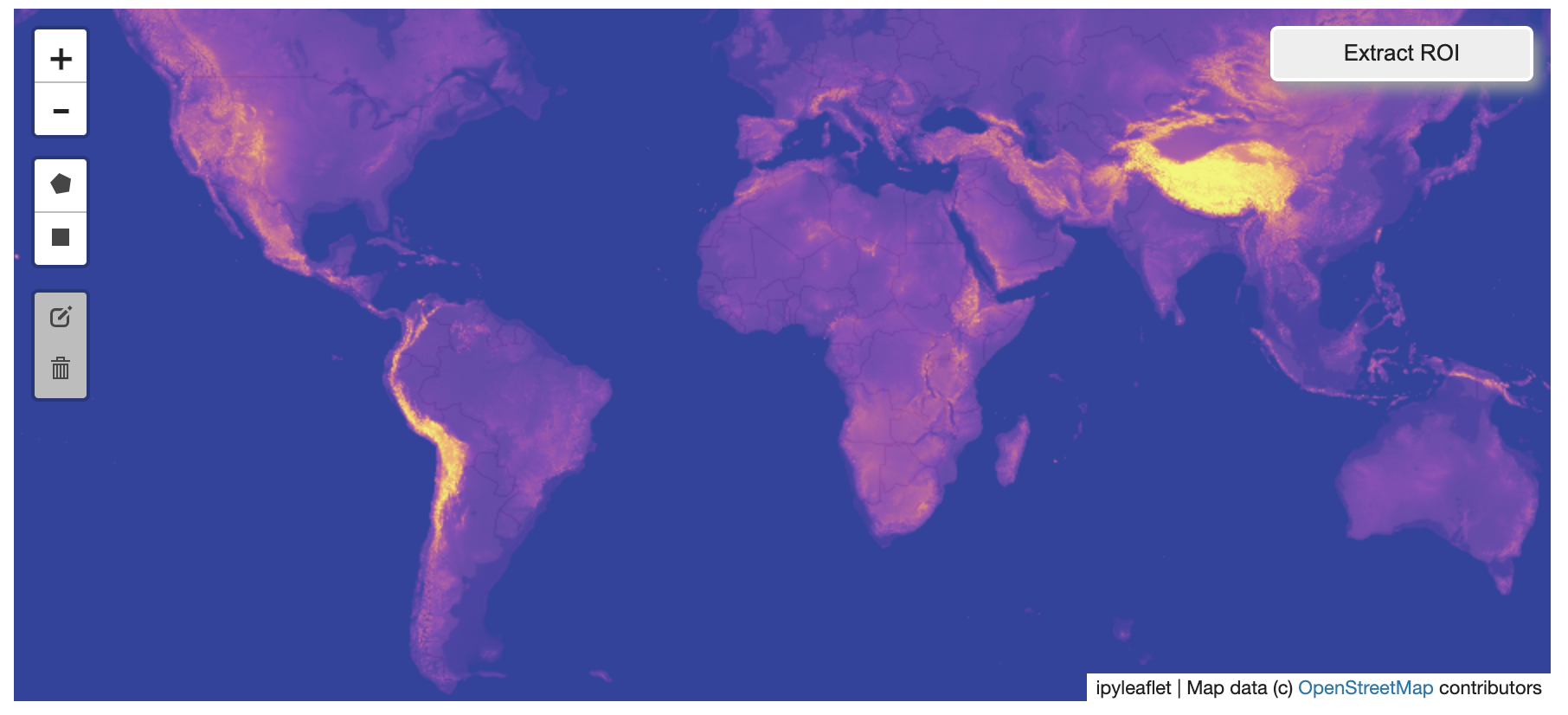
?️ Example Datasets
A few example datasets are included with localtileserver. A particularly
useful one has global elevation data which you can use to create high resolution Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) of a local region.
from localtileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, get_leaflet_roi_controls, examples
from ipyleaflet import Map
# Load example tile layer from publicly available DEM source
tile_client = examples.get_elevation()
# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server
t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client,
band=1, vmin=-500, vmax=5000,
palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6',
opacity=0.75)
# Create ipyleaflet controls to extract an ROI
draw_control, roi_control = get_leaflet_roi_controls(tile_client)
m = Map(zoom=2)
m.add_layer(t)
m.add_control(draw_control)
m.add_control(roi_control)
m
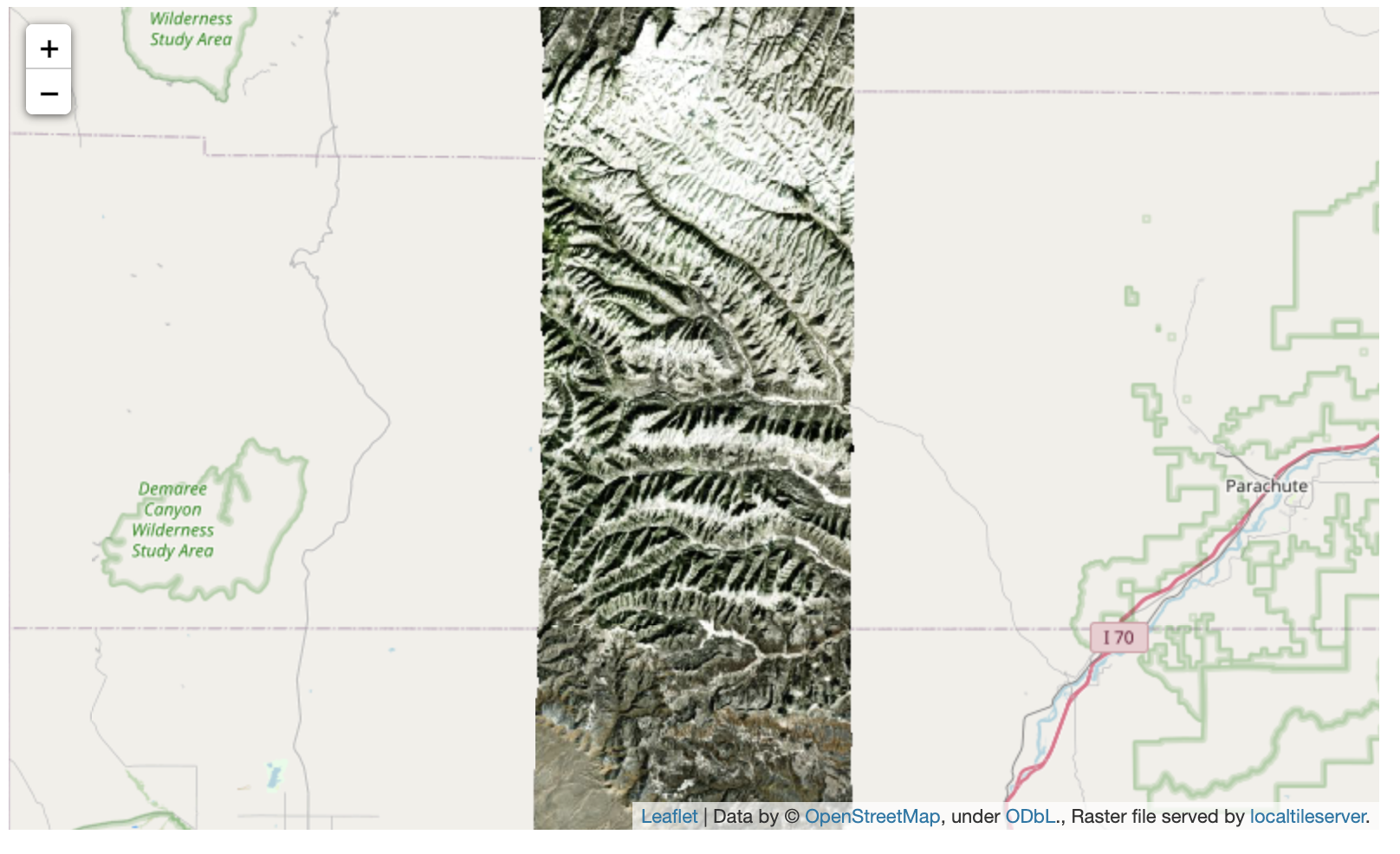
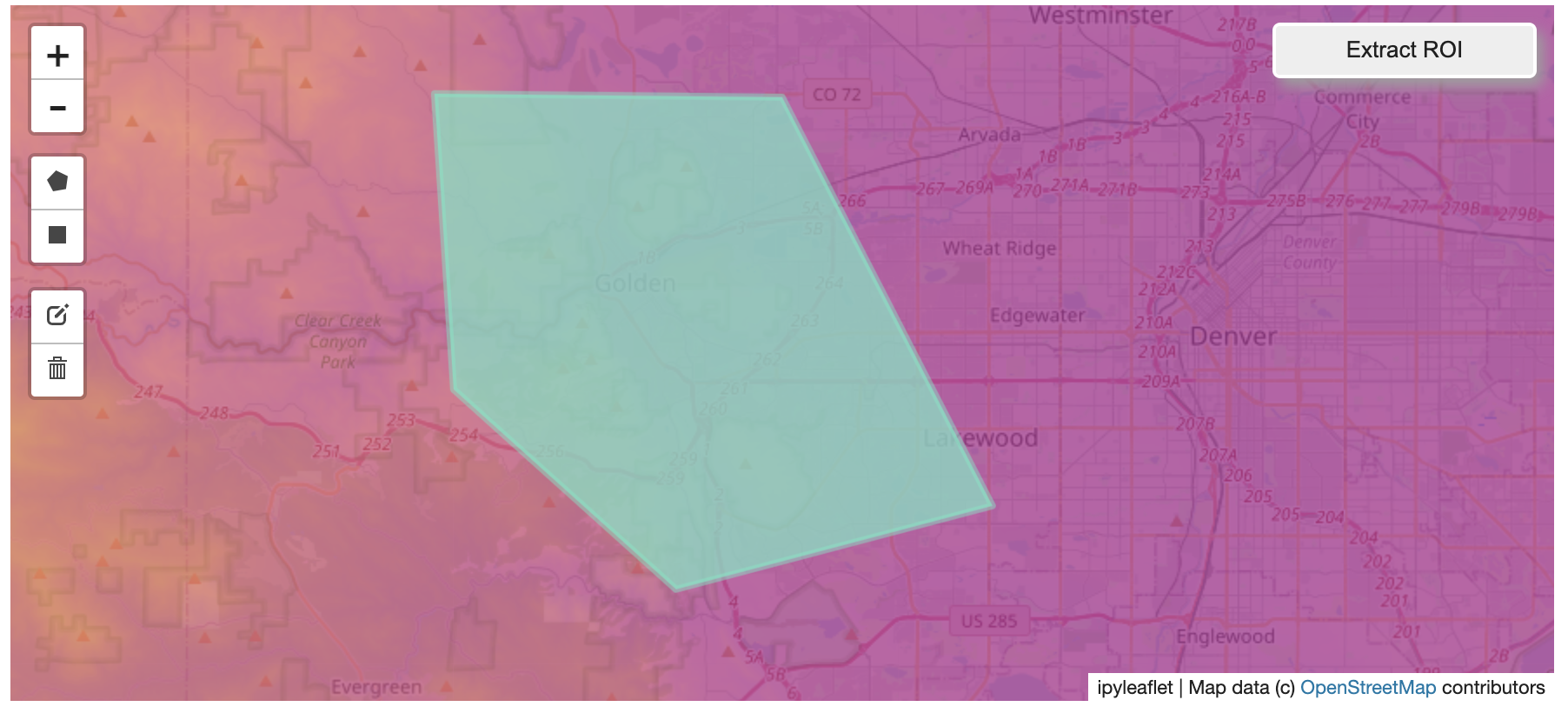
Then you can follow the same routine as described above to extract an ROI.
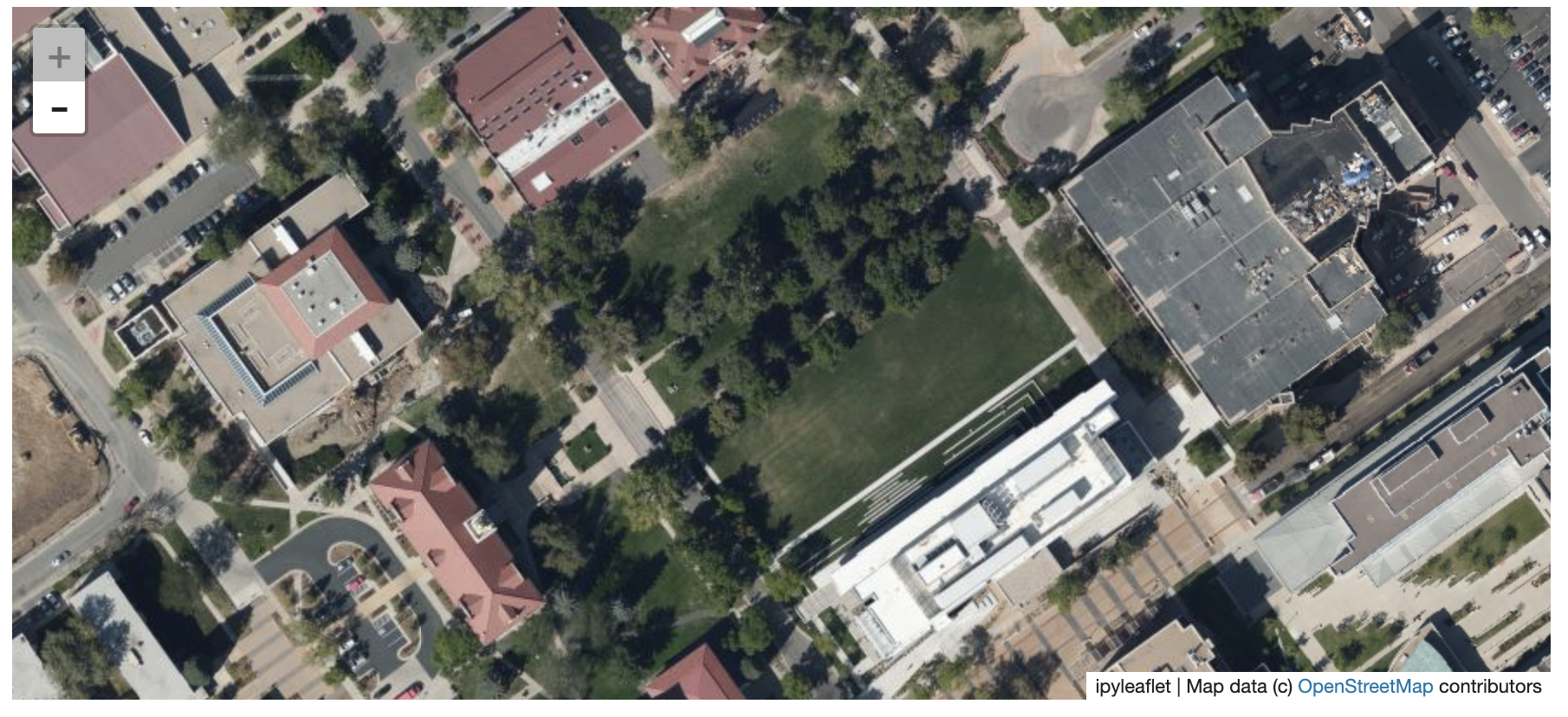
I zoomed in over Golden, Colorado and drew a polygon of the extent of the DEM I would like to create:
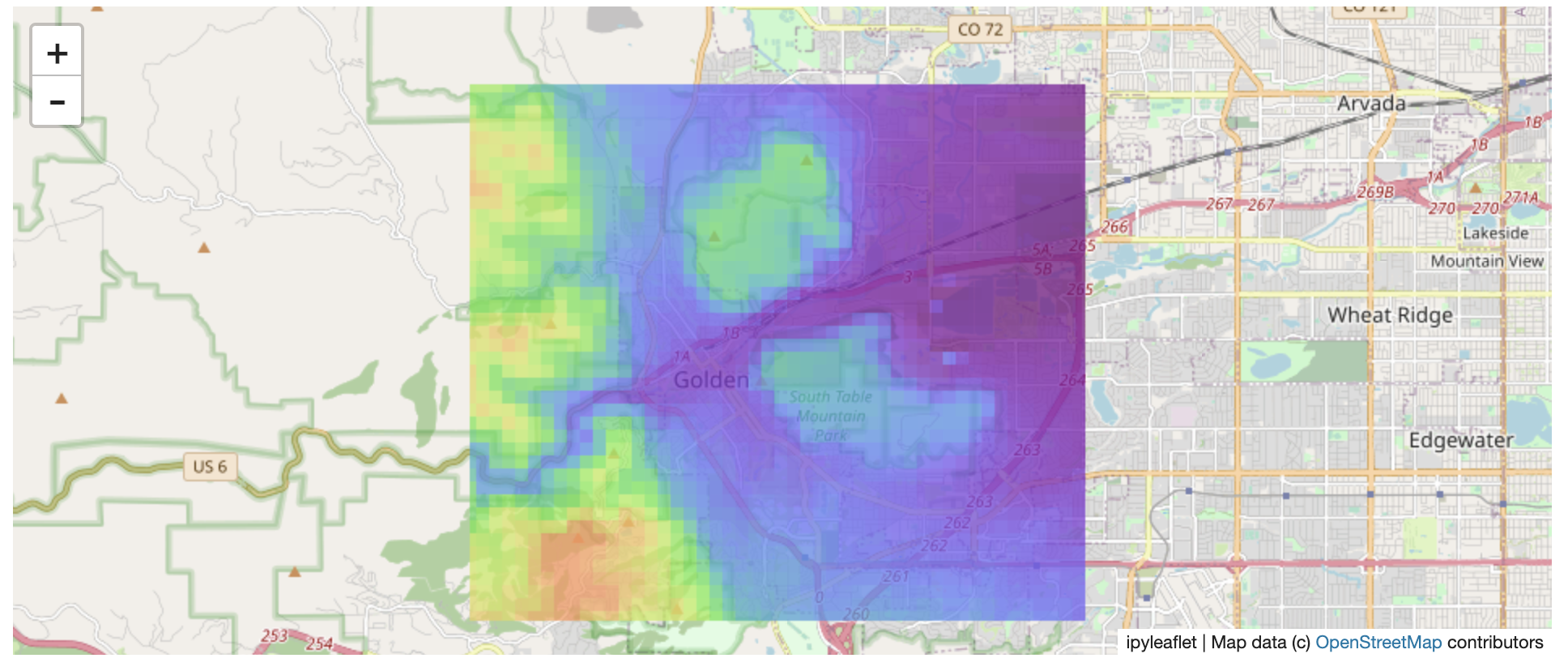
And perform the extraction:
roi_path = '...' # Look in your working directory
r = get_leaflet_tile_layer(roi_path, band=1,
palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', opacity=0.75)
m2 = Map(
center=(39.763427033262175, -105.20614908076823),
zoom=12,
)
m2.add_layer(r)
m2
Here is another example with the Virtual Earth satellite imagery
from localtileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, examples
from ipyleaflet import Map
# Load example tile layer from publicly available imagery
tile_client = examples.get_virtual_earth()
# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server
t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client, opacity=1)
m = Map(center=(39.751343612695145, -105.22181306125279), zoom=18)
m.add_layer(t)
m
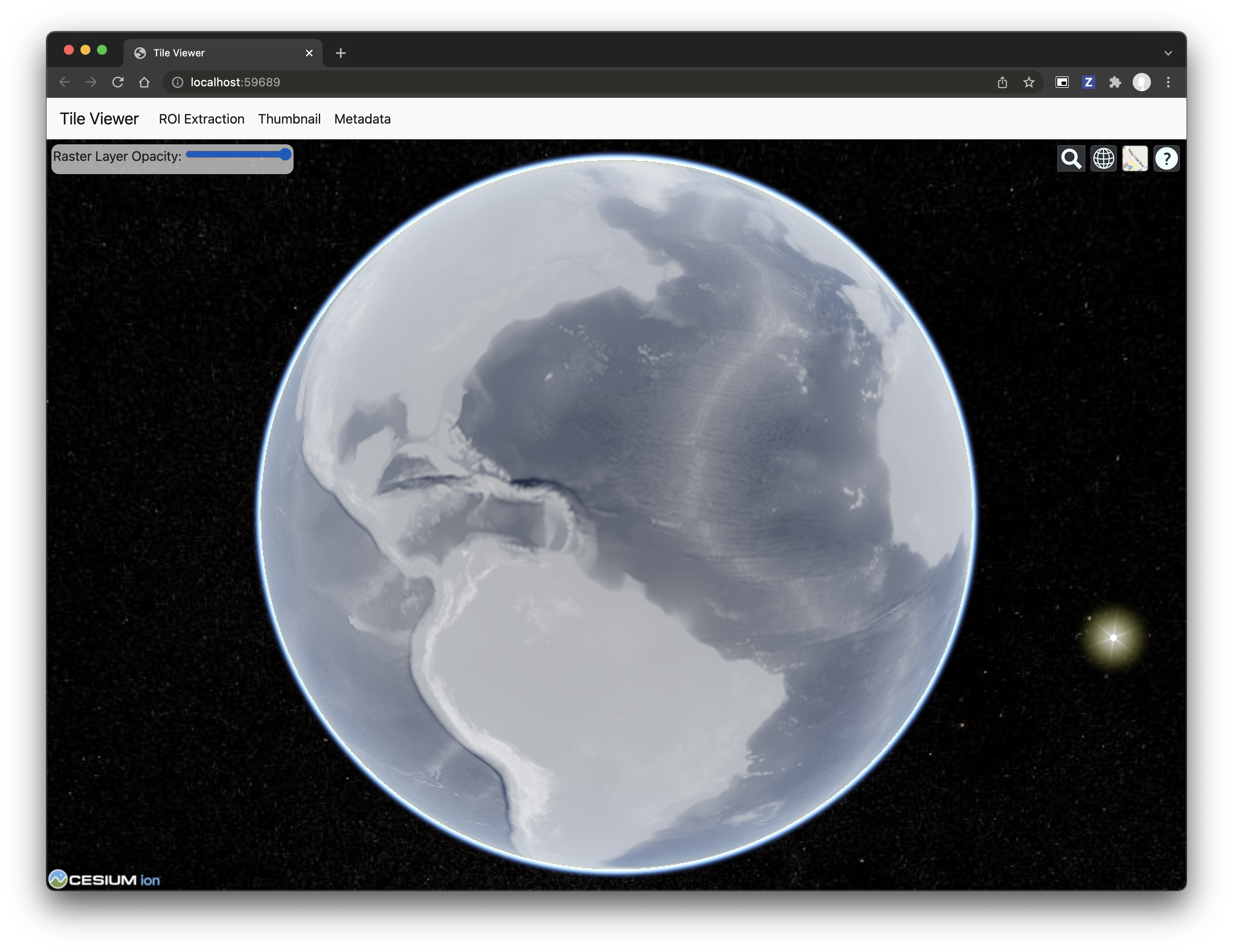
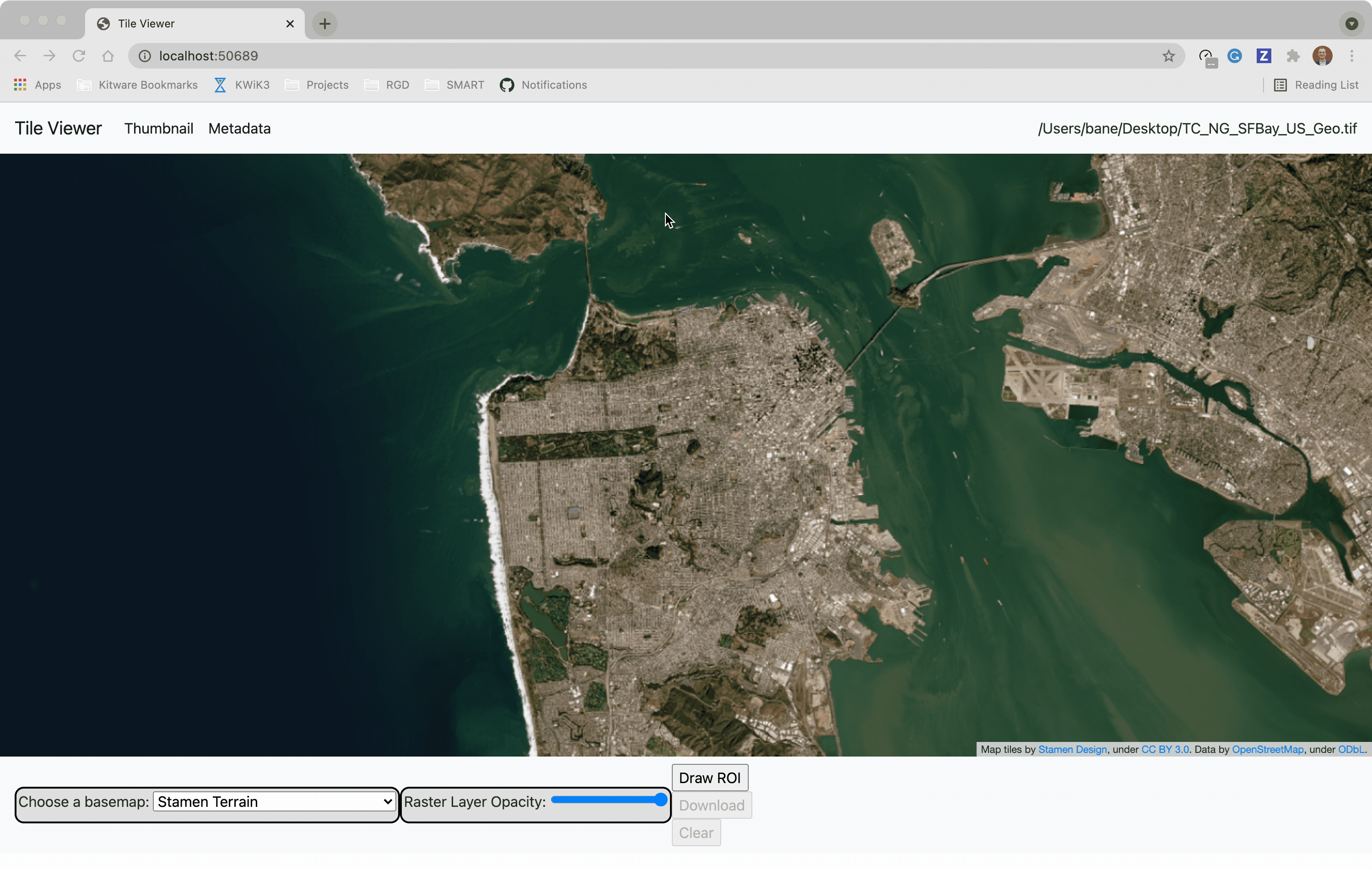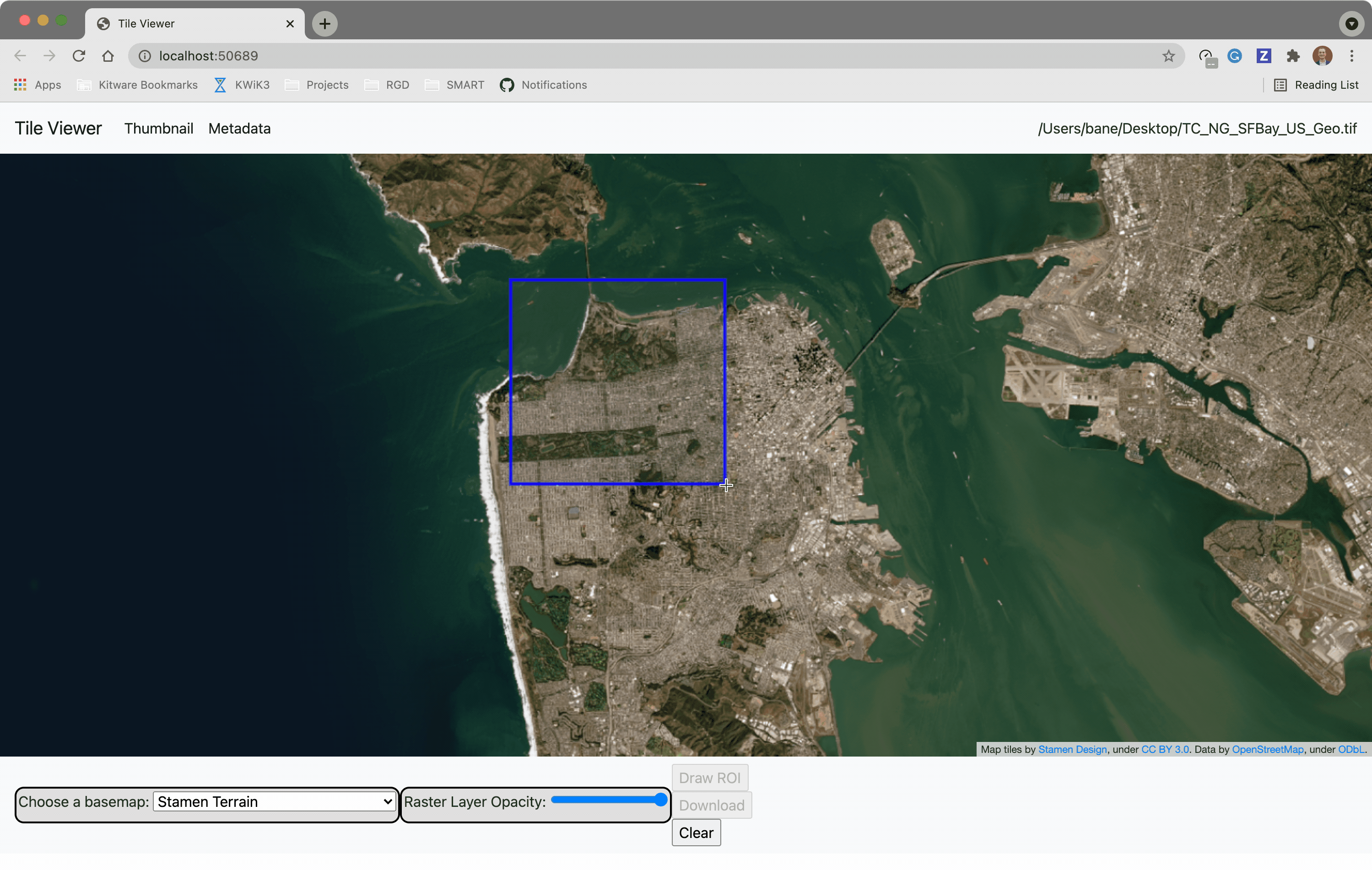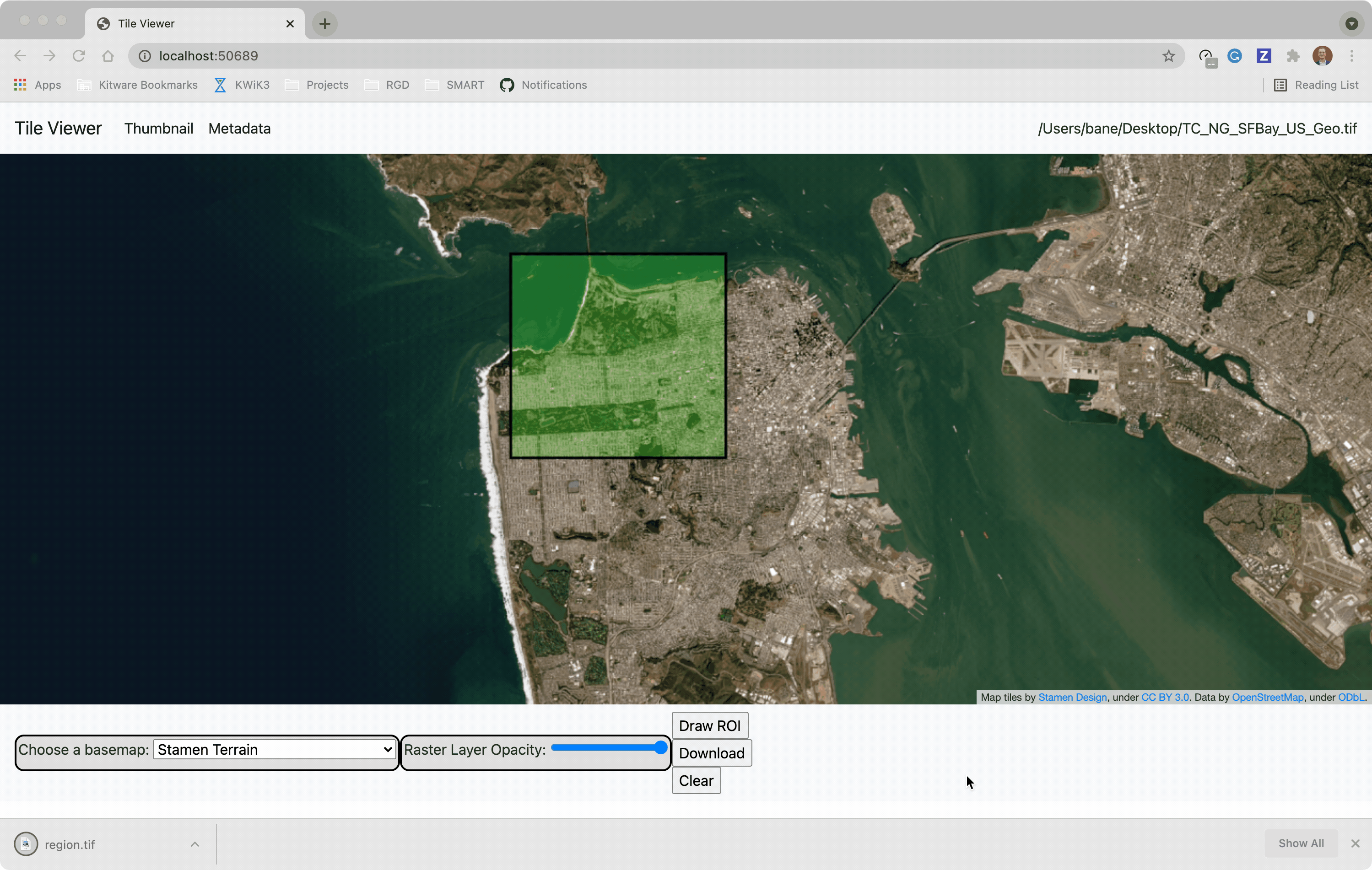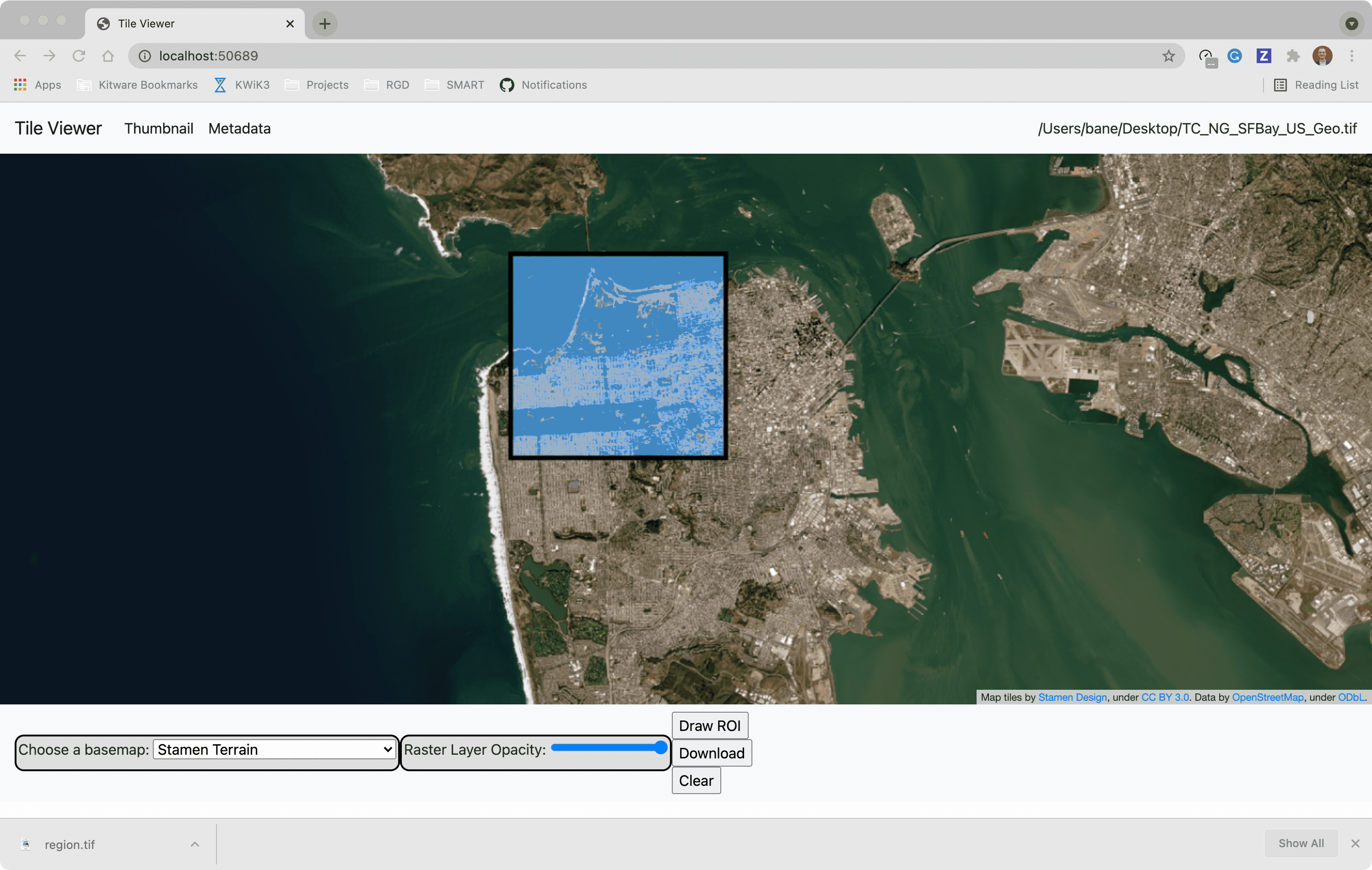
?️ Local Web Application
Launch the tileserver from the commandline to use the included web application where you can view the raster and extract regions of interest.
python -m localtileserver path/to/raster.tif
You can use the web viewer to extract regions of interest:
You can also launch the web viewer with any of the available example datasets:
python -m localtileserver dem
Available choices are:
demorelevation: global elevation datasetblue_marble: Blue Marble satellite imageryvirtual_earth: Microsoft’s satellite/aerial imageryarcgis: ArcGIS World Street Mapbahamas: Sample raster over the Bahamas
Usage Notes
get_leaflet_tile_layeraccepts either an existingTileClientor a
path from which to create aTileClientunder the hood.- The color palette choices come from
palettable.