Criteria Delete
The new feature bulk delete operation in Criteria API was added in JPA 2.1. I will show you an example how to perform bulk delete using Spring JPA CriteriaDelete. The CriteriaDelete interface can be used to implement bulk delete operations.
Delete operations performed through CriteriaDelete interface are directly mapped to database delete operations. Hence the persistent context is not synchronized with the result and optimistic lock is not available for the involved entities. Therefore, if you are using optimistic lock then you need to update the version column as part of your delete statement.
Related Post:
Prerequisites
Java 1.8+/19, Maven 3.8.2/3.8.5, Spring Boot & Spring Data JPA 2.5.6/3.1.3, MySQL 8.0.26/8.1.0
Project Setup
You can create a maven-based project in your favorite IDE or tool. The name of the project is spring-data-jpa-criteriadelete.
You can use the following pom.xml file for your maven project. The following build file has the required dependencies.
For spring boot version 3.1.3, you can use the following pom.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.roytuts</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-jpa-criteriadelete</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.1.3</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>19</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>19</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
For spring boot version 2.5.6, you can use the following pom.xml file:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.roytuts</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-jpa-criteriadelete</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>MySQL Table
For this example, I am going to create a table called product under roytuts database. So create a table product under database roytuts in the MySQL server with the below structure.
CREATE TABLE `product` (
`id` int unsigned COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`price` double COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`sale_price` double COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`sales_count` int unsigned COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`sale_date` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;I am also going to store sample data into the product table to test the application right away.
insert into product(id,name,price,sale_price,sales_count,sale_date) values(1, 'Desktop','30000','35000','55','02-10-2021');
insert into product(id,name,price,sale_price,sales_count,sale_date) values(2, 'Desktop','30300','37030','43','03-10-2021');
insert into product(id,name,price,sale_price,sales_count,sale_date) values(3, 'Tablet','39010','48700','145','10-10-2021');
insert into product(id,name,price,sale_price,sales_count,sale_date) values(4, 'Phone','15000','17505','251','05-10-2021');
insert into product(id,name,price,sale_price,sales_count,sale_date) values(5, 'Phone','18000','22080','178','05-10-2021');
insert into product(id,name,price,sale_price,sales_count,sale_date) values(6, 'Tablet','30500','34100','58','05-10-2021');
insert into product(id,name,price,sale_price,sales_count,sale_date) values(7, 'Adapter','2000','2500','68','06-10-2021');
insert into product(id,name,price,sale_price,sales_count,sale_date) values(8, 'TV','45871','55894','165','07-10-2021');application.properties
The following datasource configuration is done in the src/main/resources/application.properties file:
spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/roytuts
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true
logging.level.org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql=traceI have set the following properties so that Hibernate does not create the product table because I already have created the table in MySQL server.
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=noneI am logging SQL statement and formatting them for better reading in the console using the following key/value pairs:
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true
logging.level.org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql=traceEntity Class
The entity class maps the Java object to the table in database.
@Entity
@Table(name = "product")
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id;
@Column
private String name;
@Column
private double price;
@Column
private double salePrice;
@Column
private int salesCount;
@Column
private String saleDate;
//Getters and Setters
}Service Class
The service class is responsible for processing the business of the application.
I have included the EntityManager instance from the persistent context which will be used for building CriteriaDelete query.
An example for bulk delete may be, you want to delete all data which are older than 90 days. In this example, I am going to delete products. Though this is a simple example and in your real project you may have thousands or lakhs of records for which you want to perform bulk delete operations.
@Service
public class DeleteService {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Transactional
public void deleteBulkProducts(final String productName) {
CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder = entityManager.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaDelete<Product> criteriaDelete = criteriaBuilder.createCriteriaDelete(Product.class);
Root<Product> root = criteriaDelete.from(Product.class);
criteriaDelete.where(criteriaBuilder.equal(root.get("name"), productName));
entityManager.createQuery(criteriaDelete).executeUpdate();
}
}I am updating the product’s price based on product’s name.
@Transactional annotation from Spring framework is required on the method that performs bulk delete operations, otherwise you may get the following exception:
javax.persistence.TransactionRequiredException: Executing an update/delete querySpring Boot Main Class
Spring Boot application needs a class with main method and @SpringBootApplication annotation that will deploy the application in embedded Tomcat server.
I don’t want to use the web feature, so I am implementing CommandLineRunner interface. I also included the base package for entity class so that Spring picks it up when required.
@SpringBootApplication
@EntityScan(basePackages = "com.roytuts.spring.data.jpa.criteriadelete.entity")
public class CriteriaDeleteApp implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private DeleteService deleteService;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CriteriaDeleteApp.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("CriteriaDelete::Bulk Delete Started...");
deleteService.deleteBulkProducts("Desktop");
System.out.println("CriteriaDelete::Bulk Delete Done.");
}
}Testing the CriteriaDelete Application
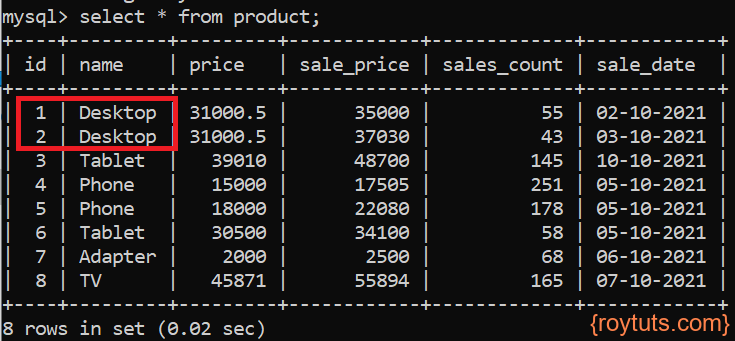
Before delete operation the records you will find in the product table are given below:
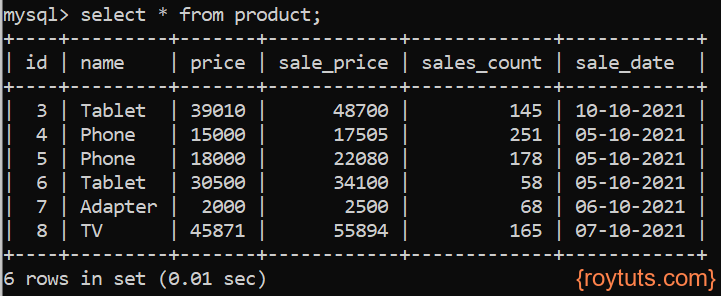
Run the above main class as Java Application or Spring Boot Application. Your products having name Desktop will be deleted.
After delete operation you will find the updated price for Desktop product:
You will also find the following log in the console for the SQL statement.
CriteriaDelete::Bulk Delete Started...
Hibernate:
delete
from
product
where
name=?
o.h.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder : binding parameter [1] as [VARCHAR] - [Desktop]
CriteriaDelete::Bulk Delete Done.Hope you got idea how to use CriteriaDelete API with Spring Boot to delete multiple records from database.